Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
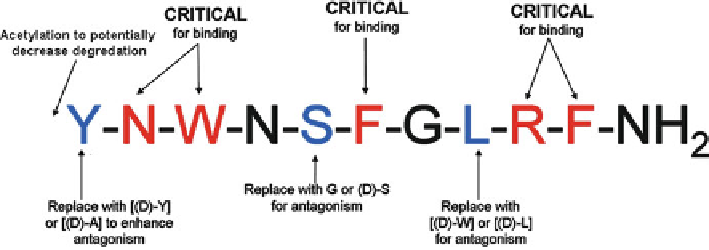
Fig. 8.9
Schematic diagram of important KP-10 residues. Residues that are important for receptor
binding (
red
) and receptor activation (
blue
) within KP-10 are highlighted
(Asn
2
, Trp
3
, Phe
6
, Arg
9
, and Phe
10
) and for receptor activation (Tyr
1
and Leu
8
).
Peptide 234 was the most effi cacious and potent antagonist in vitro.
Besides producing four antagonists, the structure-activity relationship has also
provided us with a consensus model for antagonism of KP-10 (Fig.
8.9
). The model
highlights fi ve residues involved in receptor binding (Asn
2
, Trp
3
, Phe
6
, Arg
9
, Phe
10
)
and three residues involved in receptor activation (Tyr
1
, Ser
5
, Leu
8
), which concurs
with previous alanine scanning results [
19
,
20
].
Design and In Vitro Effects of Small Molecule Antagonists
Small molecule non-peptide KP-10 antagonists containing a 2-acylamino-4,6-
diphenylpyridine scaffold have also been designed. Kobayashi et al. adopted a com-
binatorial chemistry approach to identify a 2-furoyl group to be the most active
antagonist of all tested 2-acylamino-4,6-diphenylpyridine derivatives [
24
]. They
identifi ed compound 9l (Fig.
8.10a
) with an IC
50
value of 3.7 nM for receptor binding
to KISS1R and with high antagonistic activity against KP-10 stimulated intracellu-
lar calcium release [
24
]. Then, with further optimisation, compound 15a (Fig.
8.10b
)
was designed containing a piperazine ring and exhibited high affi nity binding to
both human and rat KISS1R, with IC
50
values of 3.6 and 15 nM, respectively.
Compound 15a also showed high antagonistic activity against KP-10 stimulated
calcium release in CHO cells stably expressing KISS1R (Fig.
8.10c
) [
25
].
Compound 15a has a similar receptor binding affi nity to peptide 234 above for
human KISS1R; however, it does not antagonise calcium release to the same extent.
Peptide 234 inhibits calcium with an IC50 of 1nM and a maximal inhibition of 89%,
whereas compound 15a has an IC50 of 1
M with a similar maximal inhibition to
peptide 234. However, as compound 15a is a small molecule antagonist, it is likely
to be orally active, unlike peptide 234, which needs to be given by injection; there-
fore compound 15a may be more suitable to being taken forward into clinical
trials.
μ
Search WWH ::

Custom Search