Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
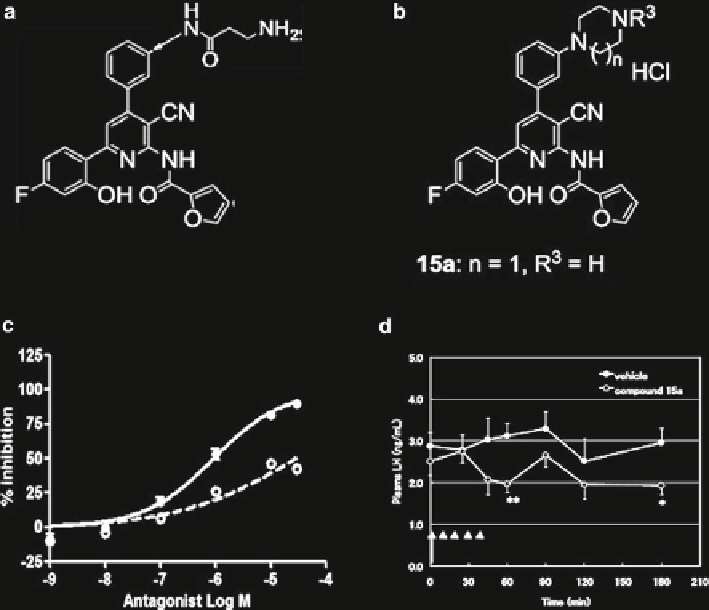
Fig. 8.10
Small molecule KP antagonist. (
a
) Structural model for compound 9l. (
b
) Structural
model for compound 15a bearing a piperazine ring. (
c
) The antagonistic activities on calcium
mobilisation of 15a (
solid line
) and 15d (
broken line
) against KP-10 in CHO cells stably express-
ing human GPR54. (
d
) Effect of compound 15a on plasma LH level in castrated male rats. Values
are means ± SE, determined from eight experiments. *
P
< 0.05 and **
P
< 0.01 compared with the
vehicle control. (From Kobayashi, T., et al., Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of
2-acylamino-4,6-diphenylpyridine derivatives as novel antagonists of GPR54. Bioorg Med Chem.
18(11):3841-59 and from Kobayashi, T., et al., 2-acylamino-4,6-diphenylpyridine derivatives as
novel GPR54 antagonists with good brain exposure and in vivo effi cacy for plasma LH level in
male rats. Bioorg Med Chem. 18(14):5157-71. Reprinted with permission from Elsevier Limited)
Testing KP's Role in GnRH Neuron Function
Since the primary action of KP is the stimulation of GnRH neurons, we determined
whether KP antagonist, peptide 234, could inhibit KP action on mouse GnRH neu-
rons in brain slices. 1nM KP markedly increased GnRH neuron fi ring activity [
26
],
as previously described [
27
]. Peptide 234 alone had no effect on GnRH neuron
fi ring, but pretreatment with this peptide at 1, 10, and 100 nM strongly inhibited
10 nM KP-10 stimulation of GnRH fi ring activity (Fig.
8.11a
). Thus, KP antagonist,
peptide 234, is a potent inhibitor of KP-stimulated GnRH neuron fi ring.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search