Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
5.2 Building Energy Simulations: A Case Study
5.2.1 Simulation Model
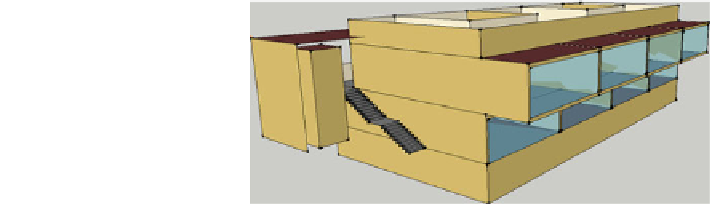
The case study is a multifunctional building (Buratti et al.
2013
), consisting of one
basement and two floors with ten zones each floor. A simplified model consisting
of eight zones (4 ? 4) was simulated (see the 3D model in Fig.
19
). Two room
types were considered for the simulations: an office room (P) at the first floor and a
commercial one (T) at the ground floor.
Both ground and first floor zones present a large glass wall in the south façade. The
opaque envelope features are reported in Table
4
. The building's thermal behaviour
was studied in the climatic and solar radiation conditions of Rome, London, Moscow,
Helsinki, Ottawa, and Beijing (different climatic zones). Figure
20
shows the
monthly mean values of the external temperatures for the chosen cities and the global
annual solar radiation. The maximum global solar radiation is related to Rome
and Beijing and the minimum value to Helsinki. During the summer period, the
maximum external temperature of London is the same as the maximum value of
Helsinki, but during winter, the differences exceed more than 10 C.
The most important simulation hypotheses are summarized in Table
5
.
The performance of different kinds of glazing was evaluated (Table
6
).
Two standard glazings were considered: a single-pane glazing (6 mm thick-
ness) and a double-glazing system with a total thermal transmittance of 5.7 and
2.7 W/m
2
K, respectively. Also a low-e glazing system with argon in interspace
was considered (glazing type 3 and total thickness 23 mm).
Fig. 19 3D model
implemented in EnergyPlus
Table 4 Opaque envelope features
Building element
U—thermal transmittance [W/m
2
Thickness [m]
K]
External wall—north façade
0.44
0.25
External wall—south façade
0.56
0.22
Internal wall
0.45
0.70
First floor
0.52
0.40
Roof garden
0.95
0.27
Roof
0.52
0.46
Ground floor
1.32
0.46