Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
(v)
be detected in 1ml. This fluorescence persists for 2-3 days. Many cations interfere in the
reaction by quenching of the fluorescence.
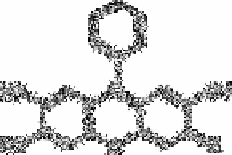
Nazarenko and Vinkovetskaya [95] studied sixteen 2,3,7-trihydroxy-6fluorones with
substituents in the 9-position as fluorescent reagents for boron. These reagents give
fluorescence reactions of low sensitivity in neutral and weakly alkaline media with boron.
The most sensitive reagent is phenylfluorone. Boron forms 1:1 complexes with
trihydroxyfluorones by replacing the proton in the reagent molecule.
A method for the determination of boron with Thoron I [2-(2-hydroxy-3,6disulpho-1-
naphthyhlazo)benzenearsonic acid (see below (vi)) has been proposed [96]. It is slightly
less sensitive than the method with benzoin, but is simpler and more precise and does not
need special precautions. This method has been used to determine boron in high-purity
silicon tetrachloride [97].
(vi)
Boric acid forms a fluorescent complex with salicylic acid [98]. Podchainova
et al.
[99]
verified that decreasing the temperature from 20 to-196°C causes the fluorescence
intensity to increase more than 10-fold. They also studied the reaction of boron with
acetylsalicylic acid [100].
Chromotropic acid (4,5-dihydroxy-2,7-naphthalenedisulphonic acid) [36] has been
proposed as a fluorometric reagent for boron. This method has a coefficient of variation
of 2.9% for 0.5mM boric acid and 5.7% for 0.0mM boric acid. The addition of masking
agents improves the selectivity of the method.
Formation of ternary complexes
Hydroxyflavones-oxalic acid
Pszonicki and co-workers [47,101-104] have studied extensively the determination of
boron with morin, quercetin and kaempferol (see below (vii-xi)) in the presence of oxalic
acid, by formation of ternary complexes.
The fluorescence of the boric acid-morin-oxalic acid complex is strongly quenched by
alkali metals. This is probably caused by a reaction of the alkali metals with the 4
′
-



Search WWH ::

Custom Search