Introduction
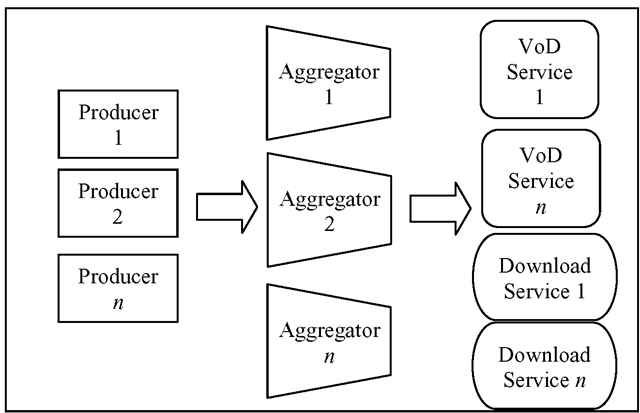
Video on demand (VoD) systems allow users to choose from a collection of titles and instantly begin to view the video material. These systems have been in use for many years but are growing in popularity recently with the expansion of digital cable and IPTV. Video download services also may use VoD-formatted content as source material. As shown in Fig. 2.12, content providers deliver content via aggregators, and these in turn provide packed content to VoD service providers.
Fig. 2.12. Video on demand content flows from producers through aggregator services and on to end-user service providers.
VoD systems support playback control including pause, fast-forward, etc., often using so called “trick streams” which are separate copies of the media encoded in advance of the content being made available for users. There may be several speeds supported and the system will switch among them to simulate advancing the video at 2x, 4x, etc. realtime. To help users make a VoD selection, services provide a preview capability and content providers prepare theatrical trailers to promote their content. To enable rapid browsing of several titles in parallel, systems present box art images of the asset along with the title. Metadata for search also includes genre, rating, actors, and a short description. Media particulars such as aspect-ratio (letterbox / full screen), existence of subtitles and captions, and alternative audio languages are also available. This collection of the media itself, a preview, box art and metadata, forms a VoD “package” which is managed as a unit; for example the package has a well defined period of availability, after which the entire package is removed from the VoD servers.
Cable Labs
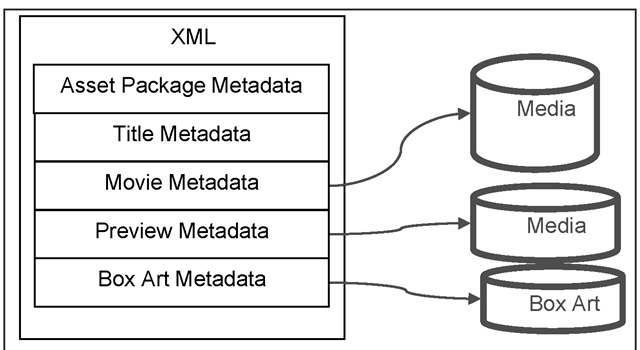
In the US, the cable companies have formed the Cable Labs, a consortium to promote standards and interoperability. Cable Labs VoD metadata and packaging standards are in widespread use for distribution of VoD content. Fig. 2.13 shows the overall structure of an ADI 1.1 package asset, while Fig. 2.14 contains a fragment of the metadata for a VoD asset in XML format. Notice that “Run_Time” has the same meaning as “total time” in Fig. 2.6.
Fig. 2.13. VoD package architecture.
Fig. 2.14. Excerpt of CableLabs ADI 1.1 format VoD metadata.