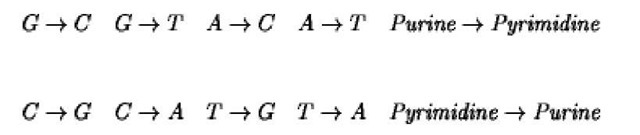A transversion mutation is a mutation that substitutes a purine for a pyrimidine or a pyrimidine for a purine, inverting the purine/pyrimidine axis of the DNA molecule. These are
Transversions may result form the mispairing of a purine with a second purine, then replication of a nascent strand completes the transversion mutation by pairing that purine with a pyrimidine. Transversions were named by Freese (1) as a class of mutations that are not easily subject to reversion by base analogs (see Transition Mutation). However, transversions typically result when a nucleotide is altered by a bulky DNA adduct so that the base-pairing capacity is lost.