4.7
Compound-wound dc motor construction is similar to series-wound dc motor construction, as shown in Fig. 4.103. The major difference is that this motor has both a series and a shunt field. The shunt field limits the maximum motor speed, in a manner similar to that in the PMDC and shunt-wound motors. The series winding increases starting torque and limits the starting current of the motor. The inductance of the series winding also helps to reduce flashover under rapid load changes.
There are two common types of compound motor connections. The long-shunt connection has the shunt winding across the power source, as shown in Fig. 4.104. Here the shunt field flux is a function of the line voltage and the shunt field resistance.
The short-shunt connection is shown in Fig. 4.105. In this configuration, the shunt winding is across the armature but in series with the series winding. Here the shunt field current is a function of the voltage across the armature and the voltage drop in the series winding. At stall there is no generated voltage in the armature, so the shunt winding sees a voltage Vsh.
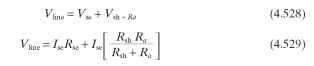
This is a function of the series winding resistance Rse and parallel combination of the shunt winding resistance Rsh and the armature resistance Ra.
As the speed increases, the generated voltage component is added, which effectively increases Ra, causing the equivalent parallel resistance to increase.This results in an increase in voltage across the shunt winding. This causes an increase in the field

FIGURE 4.103 Compound-wound dc motor field.
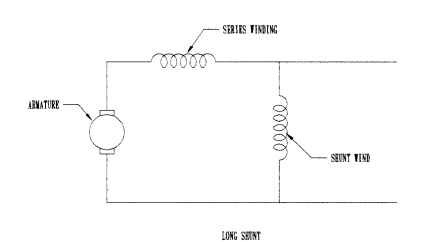
FIGURE 4.104 Compound motor long-shunt connection diagram.
flux. At the same time, the current through the series winding is decreasing, which results in a decrease in field flux.
The shunt winding turn counts for the short and long connections would have to be different to get the same resultant and field flux because of the different voltages across them.
There are two different types of compound motors in common use. They are the cumulative compound motor and the differential compound motor. In the cumulative compound motor, the field produced by the series winding aids the field pro-

FIGURE 4.105 Compound motor short-shunt connection diagram.
duced by the shunt winding. The speed of this motor falls more rapidly with increasing current than does that of the shunt motor because the field flux increases.
In the differential compound motor, the flux from the series winding opposes the flux from the shunt winding. The field flux, therefore, deceases with increasing load current. Because the flux decreases, the speed may increase with increasing load. Depending on the ratio of the series-to-shunt field ampere-turns, the motor speed may increase very rapidly.
COMPOUND-WOUND DC MOTOR CALCULATIONS (Electric Motors)
Next post: Performance Calculations (Electric Motors)
Previous post: SHUNT-CONNECTED DC MOTOR PERFORMANCE (Electric Motors)
