After the DTLS session is established, CAPWAP control traffic is encrypted and CAPWAP data traffic can be encrypted.
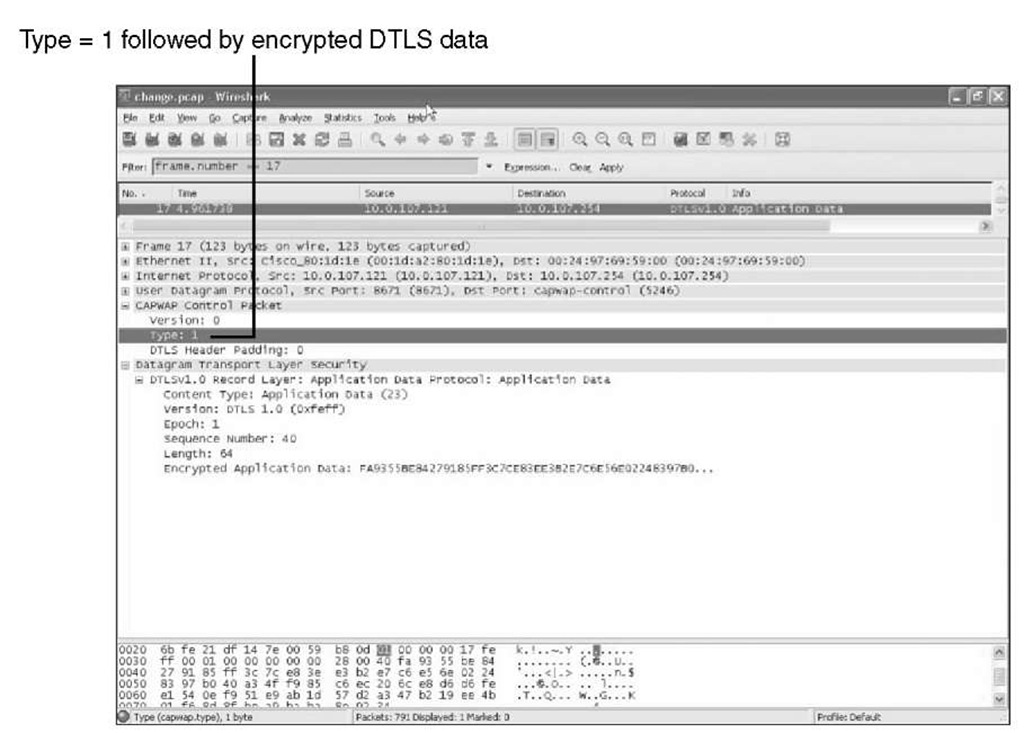
For troubleshooting reasons, it is possible to disable CAPWAP control traffic. Whether the CAPWAP control traffic is encrypted or not is controlled via the CAPWAP preamble. The CAPWAP preamble is common to all CAPWAP transport headers and is used to identify the header type that immediately follows. If the CAPWAP preamble type is equal to 0, the CAPWAP header immediately follows, which means that the packet is not encrypted. If the CAPWAP preamble type is equal to 1, a CAPWAP DTLS header immediately follows, which means that the packet is encrypted. Figure 4-10 and Figure 4-11 highlight this CAPWAP preamble type field.
Enabling or disabling CAPWAP-Control Packet encryption needs to be done on the control using the test capwap encr APNAME disable command and on the AP using test capwap dtls ctrl disable.
Figure 4-10 CAPWAP Preamble Field-Cleartext Data
Figure 4-11 CAPWAP Preamble Field-Encrypted Data
Note Those test commands are for troubleshooting purposes only and are not persistent; upon reloading the AP or the controller, CAPWAP control packets become encrypted again.
As mentioned earlier, CAPWAP-Data encryption is optional and only supported on specific hardware, such as 5508 controller and 1130 APs. CAPWAP-Data encryption is disabled by default and can be configured per AP. Example 4-4 shows how to configure and verify CAPWAP-Data encryption. The AP with the name chtac-LAP1130-04 has CAPWAP-Data encryption disabled, and the AP with the name chtac-LAP1130-03 is configured to encrypt CAPWAP-Data.
Example 4-4 CAPWAP Data Encryption