New Menu Items and Toolbars
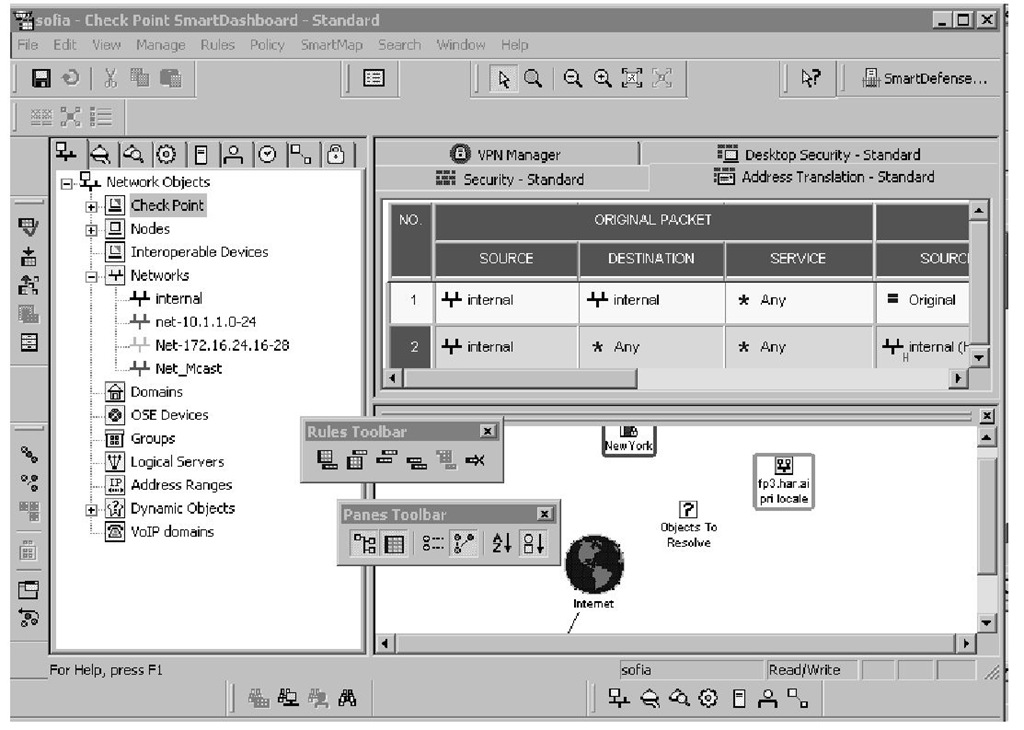
The menus and toolbars in FP3 are completely restructured. In the 4.x interface, there was a single toolbar and status bar; in the NG FP3 dashboard, we have 12 toolbars and the status bar.The dashboard exploits all Windows GUI features to manage these toolbars.
You may align the toolbars on the left, right, or bottom of the interface via drag-and-drop actions, you may have floating toolbars, and you may arrange the order of the toolbars.
The main menu items have also expanded from seven to nine, excluding the SmartMap. Some of the old functionality has been shifted to the new menu items. For example, the rule-editing submenus under the Edit menu in 4.x are organized under the Rules root menu. The changes are summarized in the following sections.
File
NG introduced revision control for security policies.The new functionality is accessible through the File menu.The printing functions now cover SmartMap:
■ New Menu Items Revision Control, Print Controls, and Delete
■ Removed Menu Items None
■ Transferred Menu Items None
Edit
Menu items for rule editing are transferred to the Rules menu. FP3 supports copying multiple objects:
■ New Menu Items Paste Object
■ Removed Menu Items None
■ Transferred Menu Items Add Rule, Delete Rule, Hide Rule, and Disable Rule
View
There is a massive change in the View menu.Toolbar changes are listed in a separate item. Queries are transferred into the Searches menu item:
■ New Menu Items Products, Toolbars, Object Tree, Object List, Rule Base, SmartMap, VPN communities, Topology VPN view, List VPN view, Reset Column Width, Sort Tree, Community Rules, Object Status in SmartMap
■ Removed Menu Items None
■ Transferred Menu Items Mask (hiding rules), Queries
Manage
UFP and CVP servers are created in OPSEC applications:
■ New Menu Items OPSEC Applications, Permission Profiles, Users and Administrators, VPN Communities, QoS, Remote Access, SmartView Monitor, User Authority
■ Removed Menu Items Users, Real-Time Monitor, Credential Manager, and Web Access
■ Transferred Menu Items None
Rules
The Rules menu is a new root-level menu; all items are new. In previous 4.x versions, the Rule Management menu items were in the Edit menu. The items in the Rules menu are Add Rule, Disable Rule, Add Section Title, Add Sub Rule, Add QoS Class, Hide, Delete, and Select All.
Policy
Policy Installation Targets, SmartDefense, and Management HA are managed through the Policy menu:
■ New Menu Items Policy Installation Targets, Convert to, View Policy of, Management HA, SmartDefense
■ Removed Menu Items None
■ Transferred Menu Items None
Search
This is a new root-level menu in FP3. Query rules directly displays the Query Clause screen.The old Query Rules screen is accessible through the Manage Query Rules item.
Toolbars
As shown in Figure 2.5, there are 12 new toolbars in NG.These organizable, floating toolbars create shortcuts for most of the menu items.The Setup VPN, Setup Extranet, and Certificates icons of prior NG versions are no longer valid. The floatable menus are:
■ New Toolbar Items Global Properties, Help, Objects, Panes, Policy, Rules, Search, Standard, Visual Tools, VPN Manager, Smart View
■ Removed Toolbar Items Certificates, VPN View, and VPN Communities
There are no major changes in the Window and Help menus. When SmartMap is licensed, a full-featured SmartMap menu is also displayed.
Figure 2.5 SmartDashboard Toolbars
New Object Types
Object types help firewall administrators have organized control over the various objects. Obsolete object types are retired, but the new NG object types truly reflect Check Point’s approach to granular firewall administration. This massive change required a change in the underlying file types such as objects. C file. There are three new object type categories: OPSEC Applications, Virtual Links, and VPN Communities.The 4.x Object Type categories User on Account Unit and Keys are not valid in NG. All the changes in each object type category are summarized in the following sections.
Network Objects
"I can’t define my third-party firewall" is a typical discussion group post for the experienced 4.x firewall administrator.The missing workstation object is the next question.
In the new NG network object type hierarchy, all Check Point installed products are under Check Point object types.This includes single interface boxes, clusters, embedded devices (also known as integrated firewalls), routers, and switches.The remaining network components can be defined under "Node," which replaces the old workstation and gateway products.
If VPN is required between a third-party node and the FireWall-1/VPN-1 protected network, the external node must be defined as an interoperable device, such as Cisco PIX.The access control list (ACL)-based routers and switches are defined as
Open Security Extension (OSE) devices.The new object type categories are dynamic objects and the voice over IP (VOIP) domains.
Services
There isn’t a significant change under this category at the object type level. When you browse this category, you will notice a group called Compound TCP Services.This type is a predefined group for FloodGate-1. DCE-RPC services have been recoded in NG and they are much more functional. Although they need to be defined explicitly in the Rule Base, they have a finer control on the traffic. DCE-RPC is now a separate object type.The port range object type of 4.x is not valid in NG. In NG, port ranges are defined by adding a hyphen between the lowest and the highest port numbers in the TCP or UDP service properties window’s port field. When you’re defining port ranges, it is possible that two services could be using the same port number. If the service field of a rule is Any, all services will match this rule, including the ones with port ranges.To avoid this problem, uncheck Match for Any for the services, which use the same port.This property is defined in the TCP Properties window.
Note
If Keep connections open after policy has been installed is checked, all control and data connections will remain open until the connections have ended, even if they are not allowed under the new policy. This overrides the settings in the gateway’s Connection Persistence page.
If you change this property, the change will not affect open connections, only future connections.
Resources
Besides URI, SMTP, and FTP resources, NG offers three new resource object types:
■ URI for QoS A resource for FloodGate-1 Rule Base.
■ TCP resource Any generic TPC service traffic may be piped to CVP or UFP traffic with this resource.
■ CIFS resource A resource for stateful inspection of the new disk share access over Common Internet File Sharing (CIFS) protocol.
OPSEC Applications
The process of defining a CVP or UFP server has been changed.Another supported feature is the support for multiple OPSEC servers.You may scale your OPSEC-based servers via chaining or load sharing. Chaining requires splitting the inspection tasks on multiple servers, but load sharing distributes the requests on identical servers with a round-robin algorithm.The server groups are also formed under the OPSEC Applications menu.
Servers
Though the basic server types remain unchanged, the submenus are more stable. It is easier to define directory servers under LDAP Account Unit. The UFP and CVP server definitions have transferred to OPSEC Applications, and Defender and Policy Server types are no longer valid. SecuRemote DNS Server may be defined through the Servers menu as well.
Users and Administrators
Managing administrator users through SmartClients was an eagerly awaited functionality. It is now possible to define administrator users and user groups through SmartDashboard (see Figure 2.6).
Figure 2.6 Users and Administrators
Another important change in FP3 is the Generic* user. If you try to create this user, your request will be denied since it is predefined.To manage Generic* users, you should use the External User Profile object type.
When you define directory services through servers, you will be able to modify the user settings through the Users and Administrators category under the Object Tree.
Time
Time objects and groups are accessible through the Time menu.The new Time object type is Scheduled Event. Scheduled Event objects are used to trigger processes, for example, in the Management High Availability page of the Global Properties window and in the Logging Policy page of the Workstation Properties window.
Virtual Links
The new virtual links are created in SmartDashboard. With virtual links, it is possible to monitor traffic and service-level agreements (SLAs) between two network entities. Monitoring virtual links is detailed in the "SmartView Monitor" section later in this topic.
VPN Communities
The new VPN Communities, which allow VPN Communities as a matching factor in Security Rules may be defined through this object type category. Site-to-Site, Extranet, and Remote Access are the available object types.
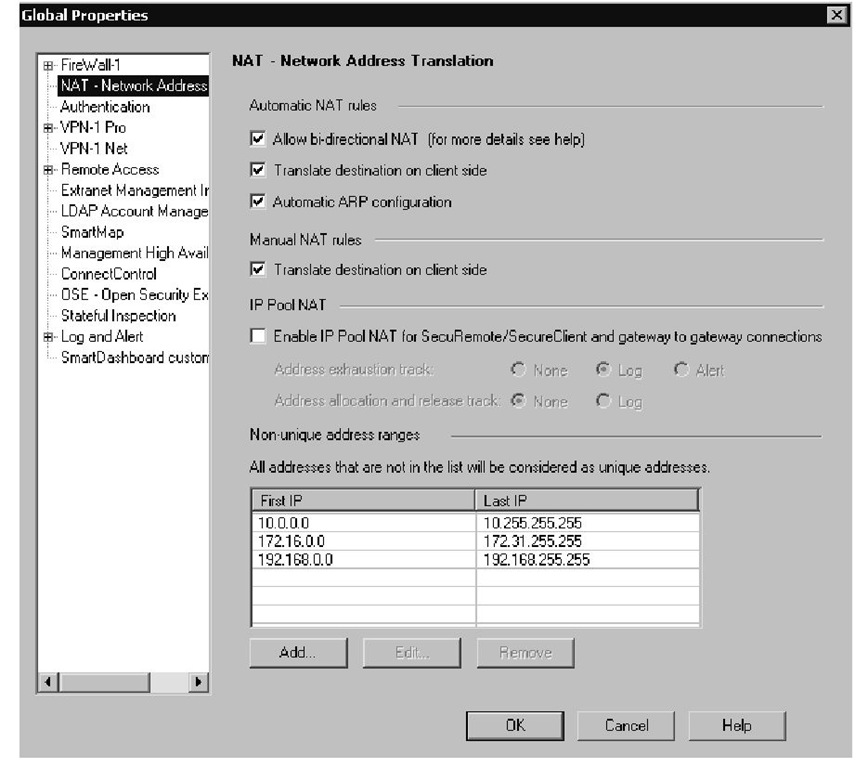
The Extended Object Properties Screen
The Global Properties window in Check Point GUI client 4.1 release had 13 tabs layered in three lines. Check Point’s GUI developers have addressed this problem by introducing "Windows-style" expandable left pane navigation trees.The tabular GUI view in the overpopulated menus of Global Properties, Check Points, Nodes, Interoperable Devices, Time, and VPN Communities windows have been replaced by a expandable tree pane on the left side of the window.You may manage all properties from this expandable GUI (see Figure 2.7).
Figure 2.7 The New Menu Style in Global Properties
Extended Administrator Access
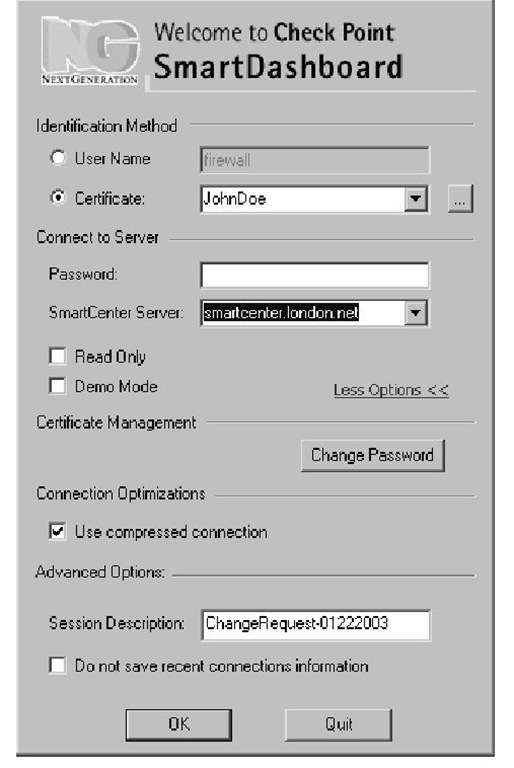
Now it is possible to use your certificates to authenticate your GUI access. In the SmartDashboard login screen, you may choose to use your certificates or change your certificate password (see Figure 2.8).
Another important improvement is the Demo Mode. Every SmartClient installation comes with a predefined demo network. When the Demo Mode check box is selected, the other options are grayed out and you make a local logon to the demo security rule base. This semifunctional rule base is very helpful for learning the features when lab facilities are limited.
Figure 2.8 The GUI Client Login Window
Tools & Traps…
Editing the Demo Database
The SmartClients installation folder contains the demo database in the following folder:
This folder contains authentic objects_5_0.C and other files so you can modify and change the actual demo files. For troubleshooting purposes, you may view other policies simply by changing the contents of this folder.
The last new function on the logon screen is the Session Description.This free text area is very useful when combined with the security policy. This text is directly logged under audit log type when logout is executed. In other words, it is possible to comment the SmartDashboard sessions in the log database.This text is visible when Session ID is checked in SmartTracker.