Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Z
DR
HOLE
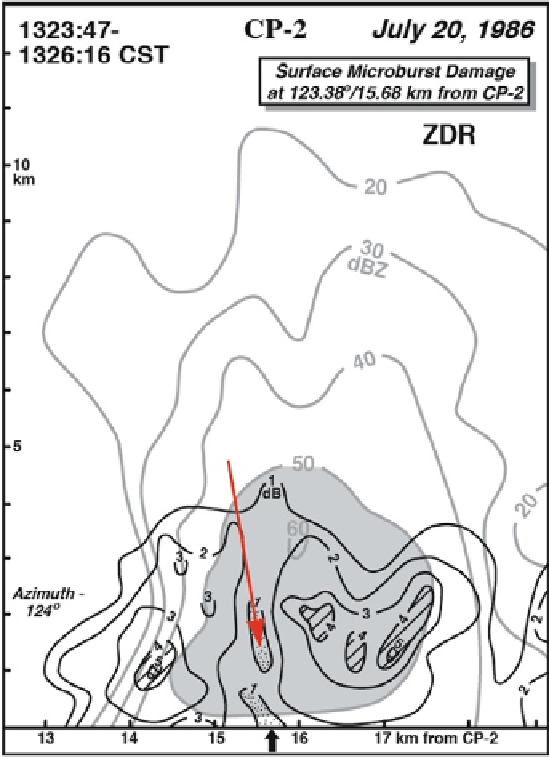
Figure 3.26. Z
DR
hole in a microburst in Alabama as depicted by data from the NCAR CP-2
Doppler radar (at S-band) during MIST (Microburst and Severe Thunderstorm Project). The
radar reflectivity factor is given by thin lines and labeled in dBZ; differential reflectivity Z
DR
is
given by thick lines and labeled in dB. The location of damage is indicated by the arrow at the
surface (from Wakimoto and Bringi, 1988).
wavelength) Doppler radars (the Terminal Doppler Weather Radar, TDWR), and
installed them at major airports to aid in warnings of microbursts. With the
advent of polarimetric radars, the melting of graupel and resultant water-coated
Raindrops tend to have relatively high differential reflectivity because they flatten
as they fall. When low Z
DR
is found just above a region of high Z
DR
near the
melting layer, it is likely that melting of precipitation is occurring. A narrow
region of high reflectivity aloft and low differential reflectivity is indicative of a
Search WWH ::

Custom Search