Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 14
Input wave form at acceleration 250 gal.
caused by the reinforcement preventing an initial increase in pore water pressure
and less settlement of the crest. When the pore water pressure increased to the
effective overburden pressure, settlement with reinforcement did not increase as
rapidly as without reinforcement. This would indicate that reinforcement with
continuous fibers or together with sheet piles may greatly decrease settlement of
existing embankments on liquefiable foundations.
Though the results from the models cannot be applied directly to actual
structures, this method may offer an advantageous construction method
providing earthquake resistance for existing earth structures.
2.3 Analysis of the Shaking Table Tests
The effectiveness of reinforcement with continuous fibers was confirmed by the
shaking table tests, and the following is an analysis of the effectiveness by
simulation of the large shaking table test. The dynamic analysis program
“DIANA-J2” was used.
2.3.1 Method of Analysis
The constitutive low used in the analysis was the Densification model, which uses
Endochoronick equations to show an increase in pore water pressure. The model
assumed a total strain, e, given by the effective strain, e
0
, and the autogenious
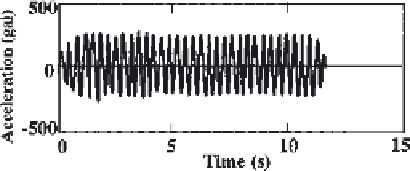
Figure 15
Acceleration at A1 [Case (a)].
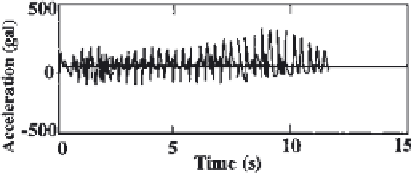









Search WWH ::

Custom Search