Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
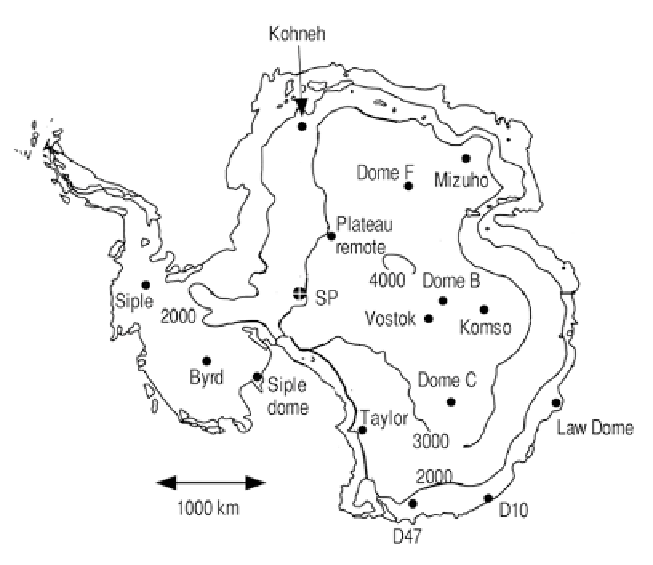
Figure 4.8. Antarctic topographical map showing the locations of several major ice core sites
(adapted from Oard, 2005).
bisected into two unequal parts by the Transantarctic Mountains. The larger East
Antarctic Ice Sheet (EAIS) contains 26 million m
3
of ice—enough to raise global
sea level by 60m if it melted. The much smaller and less stable West Antarctic Ice
Sheet (WAIS) contains 3 million m
3
of ice and could contribute 7m to global sea
level rise (Naish).
Figure 4.8
provides a rough topographical map showing the locations of
several major ice core sites in Antarctica. The characteristics of the various drilling
land, averaging about 5 cm/year over the main dome area (Dome F to Dome C).
However, it reaches over 60 cm/year of water (equivalent) near Law Dome on the
coast. Temperatures are much colder than in Greenland—for example, the average
temperature at Vostok is
55
C.
Masson-Delmotte et al. (2010) revisited EPICA Dome C data and made
several new additions. They corrected previous temperature estimates for the
change in elevation, as shown in
Figure 4.11
. They also characterized each of the
last eight interglacial and glacial maximum periods in terms of temperature, CO
2
,
dust, and other variables.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search