Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Sirsa
Irrigation
Circle
India
W
1
a
Bhakra
Main Branch
W
3
Mammarkhera Dy.
Sukhcha in
Distributary
.
Bani
Sirsa
Sirsa Major Dy.
Otty
Ellenabad
Dy.
W
2
0
10 Km
Gigroni
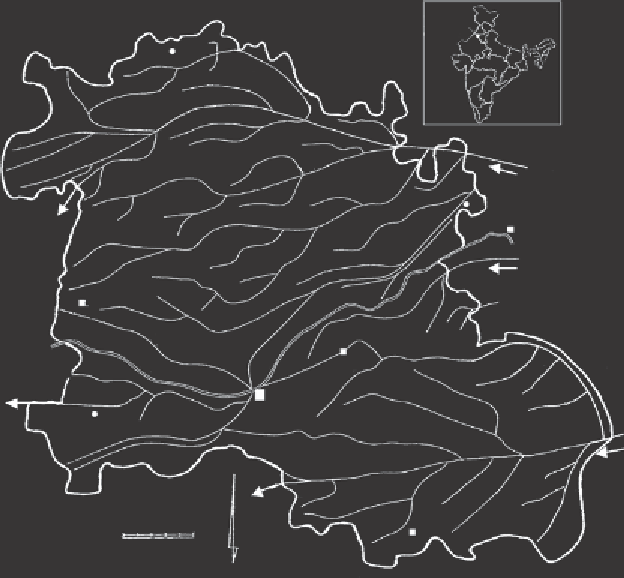
Figure 8.5
Location and canal network of Sirsa District.
experimental stations. These water management problems made Sirsa District a suit-
able pilot area for a water productivity analysis.
8.3.3 Modelling Tools
The ecohydrological model SWAP (Soil, Water, Atmosphere, Plant;
Chapter 9
) has
been used to simulate water and salt transport in the soil and crop growth in rela-
tion to weather and irrigation data. In addition, the satellite image processing model
SEBAL (Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land) has been used. SEBAL calcu-
lates actual and potential evapotranspiration rates from cropped and bare land (Bas-
tiaanssen et al.,
2005
). The key input data for SEBAL consist of satellite images
with spectral radiance in the visible, near-infrared and thermal infrared part of the
spectrum. SEBAL computes a complete radiation and energy balance along with the
resistances for momentum, heat and water vapour transport for every individual pixel.
The resistances are a function of physical conditions near the soil surface, such as soil
hydraulic head (and thus soil moisture and soil salinity), wind speed and air temper-
ature. Satellite radiances are converted irst into land surface characteristics, such as
surface albedo, leaf area index, vegetation index and surface temperature. These land
Search WWH ::

Custom Search