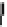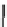Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
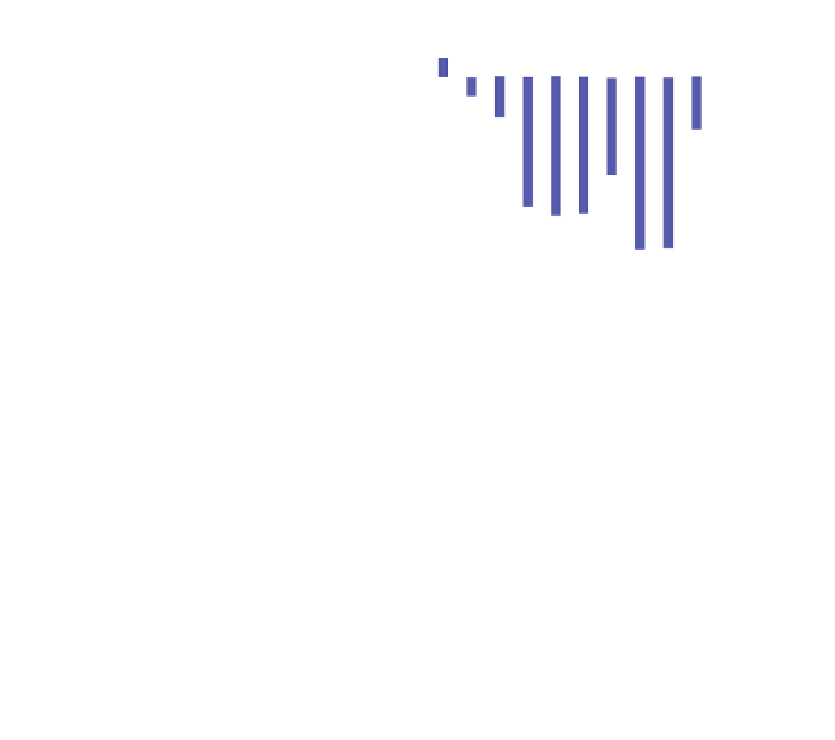
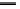
Fig. 2 Climate characteristics of
the 14 major Arctic basins. The top
panel shows average annual
temperature; the bottom one shows
annual average precipitation, for
the periods 1961-1990 and
1991-2009. Data from CRU
(Harris et al.
2013
)andWillmott&
Matsuura (
http://climate.geog.
udel.edu/*climate
)
. Precipitation
values are averages of original data
and data with orographic and un-
dercatch corrections (Adam and
Lettenmaier
2003
;Adametal.
2006
)
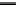
X
n
MAE
¼
1
W
w
i
e
jj
i
¼
1
where e
i
= P
i
- O
i
is the difference between the model-projected value P
i
and the
observed value O
i
for all cells i = 1, 2, … , n within the basin. The term w
i
denotes the
area-relative weight of each cell and W the sum of these weights. Similarly, the MBE
describes the area-weighted sum of the deviations of model projections from observations,
but retains the signs of the differences:
W
X
n
MBE
¼
1
w
i
e
i
i
¼
1
In comparing models across several drainage basins or for several parameters, a
dimensionless index of model performance can complement the MAE and MBE, which are
both defined in the units of the studied model parameter. We therefore also calculate such a
dimensionless measure: the refined index of model performance d
r
, with values on a
unitless scale from -1 to 1 (worst to best). The d
r
index is comprehensively defined in
Willmott et al. (
2012
), and in their words, ''[i]t indicates the sum of the magnitudes of the
differences between the model-predicted and observed deviations about the observed mean
relative to the sum of the magnitudes of the perfect model (P
i
= O
i
, for all i) and observed
deviations about the observed mean.''