Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 4.153
View from above of Bénard convection cells in a thin
layer of oil heated uniformly below: the convection is driven by
inhomogeneities in surface tension rather than buoyancy. The
hexagonal cells with flow out from the centers are visualized by light
reflected from Al-flakes.
Fig. 4.154
Circular buoyancy-driven convection cells in silicone oil
heated uniformly from below in the absence of surface tension.
Fig. 4.155
Rayleigh-Bénard convection cells in a rectangular box filled with silicone oil being heated uniformly from below. The convection is
due to buoyancy in this case.
Fig. 4.156
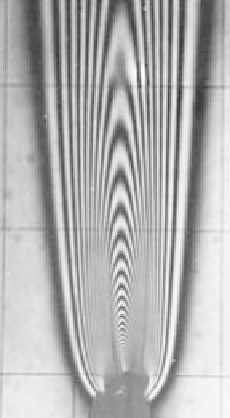
Isotherms in a plume sourced from a heated wire and
shown by an interferogram. Plume grows outward as the
2
⁄
5
power of
height.
Fig. 4.157
Isotherms of a laminar plume formed by convection
around a heated cylinder in air.





















Search WWH ::

Custom Search