Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
particular period of time. It is also possible to generate probability laws that can be
used to work out average rainfall and reduction coefficients.
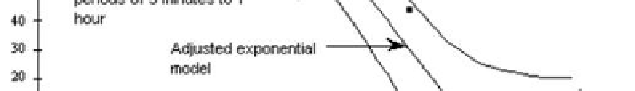
Rain gages used in
Nancy, France, for
periods of 1 hour to
6 hours
Rain gages used in
Rungis, France, for
periods of 5 minutes
to 1 hour
Adjusted exponential
model
Figure 7.12.
The function of the structure of rainfall in the
regions of Paris and Lorraine in France
For example, we analyzed the correlation coefficients (referred to as r) that were
produced by Bergaoui and Desborde in Rungis, near Paris [BER 87]. Bergaoui and
Desborde used a set of rain gauges that recorded data over different time periods,
ranging from 5 minutes up to 1 hour. Regarding the correlation coefficients for the
Urban District of Nancy, the rain gauges that were used also recorded data over
different time periods, from 1-6 hours. The correlograms produced can be adjusted
so that they can be used with exponential models and so that the parameters of p
vary as a function of duration of time. The following equation is, therefore, used to
describe the entire set of observations:
h
−
=
(
h
is expressed in meters and t is expressed in minutes)
0.42
1,530
t
rht
(,)
e
For a drainage basin whose shape is considered as being square we have seen
that:
σ
0
245
S
S
=
1 −
,
σ
p
which leads to:
σ
0.245
S
=−
1
S
σ
1, 5 3 0 t
0.42