Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
If average rainfall present in the drainage basin follows a Gumbel law, the
following is true:
−
(
x
−
x
)
/
g
−
e
oS
S
F
(
x
)
=
e
s
with
g
=
0
78
σ
and
x
=
m
−
0
577
g
or:
S
S
oS
S
[
{
}
]
x
=
x
+
g
−
Ln
−
Ln
(
F
)
oS
S
S
F
Whenever the value of the frequency is closer to one, the second variable is
predominant and the equation can then be written as:
{
[
]
}
x
≈
g
−
Ln
−
Ln
(
F
)
S
S
F
[
]
{
}
x
≈
0
78
σ
−
Ln
−
Ln
(
F
)
S
S
F
This is also true for isolated rainfall:
{
[
]
}
x
≈
0
.
78
σ
−
Ln
−
Ln
(
F
)
p
F
and for more uncommon frequencies, the reduction coefficient K (S,t) becomes:
K (S,t) = x
F
S
/ x
F
P
=
σ
S /
σ
S
K( S, f )
=−
1
36
t
042
.
where
S
is measured in kilometers square
and
t
is measured in hours.
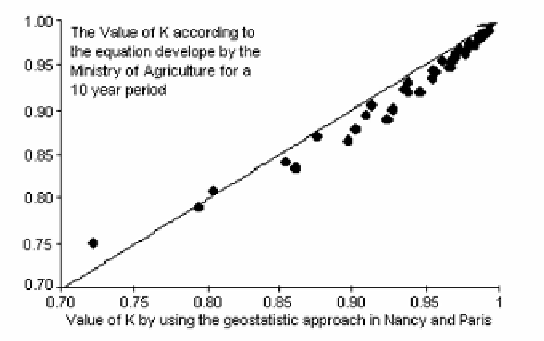
Figure 7.13.
A comparison of the results from traditional
and geostatistic approaches