Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
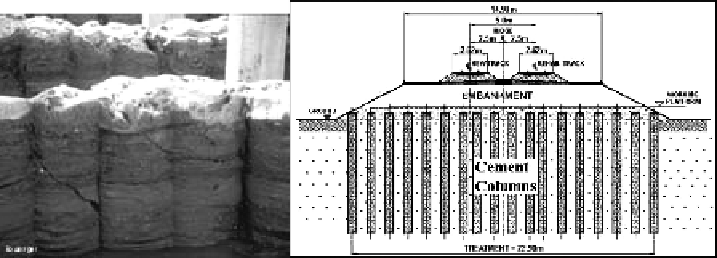
Figure 6.18
Cement mortar providing strength in CDM and the soft soil being solidified (
after
Raito
Kogyo, 2006; Huat, 2004).
the cement slurry. Figure 6.18 shows the shape of cement mortar after strengthening.
A series of overlapping augers ensures that the main geotechnical purpose will be
achieved (Kazemian and Huat, 2009b).
CDM is a soil stabilization method which mixes cement slurry with soft soil
in situ
to attain the required strength. Soft soil is stabilized by a two-phase chemical reaction.
A hydration reaction occurs and an ettringite of capillary crystals is generated when the
cement mixes with water. Then a pozzolanic reaction follows, whereby the hydration
product reacts with the clay minerals in the soil (Raito Kogyo, 2006).
6.4.3 Jet grouting systems
Jet grouting systems, the third type of DMM method, have some similarities with the
previous methods. This method has been used for soft clays. Apart from having the
same mixing tools, this method also applies the same process, whereby the
in situ
soil
will be cut and broken by a high pressure jet of slurry to produce a homogeneously
improved zone around the mechanically mixed core.
6.4.4 Vacuum grouting injection
It is worth pointing out that pressure injectionmay be less successful when the pressures
needed to dispel gases and liquids from the voids are so high as to risk disrupting the
structure. For instance, this may happen when the voids consist of many fine interstices
which do not always interconnect (which may result in the need for a very large number
of injection points), when complete filling is very difficult to achieve, or when it is
difficult to confine the grout to the area to be injected.
The third step in single-phase jet grouting is vacuum grouting injection. In this
technique, a partial vacuum is first established in a portion of the structure (or the
whole of the structure if it is small enough), drawing off gases and liquids from the
voids and interstices.
This vacuum holds the structure together, rather than exerting any potentially
disruptive forces as in pressure injection. After achieving a stable vacuum, the injection