Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
22.4.1 b
ernoulli
'
s
e
quation
In a hydraulic system, total energy head is equal to the sum of three individual energy heads. This
can be expressed as
Total Head = Elevation Head + Pressure Head + Velocity Head
This can be expressed mathematically as
2
Ez
p
w
V
(22.16)
=+ +
2
g
where
E
= Total energy head.
z
= Height of the water above a reference plane (ft).
p
= Pressure (psi).
w
= Unit weight of water (62.4 lb/ft
3
).
v
= Flow velocity (ft/sec).
g
= Acceleration due to gravity (32.2 ft/sec
2
).
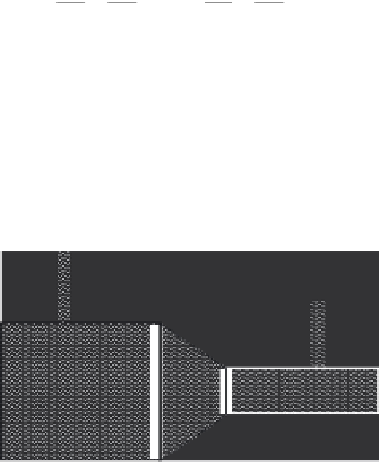
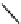
Consider the constriction in the section of pipe shown in Figure 22.4. We know, based on the law
of energy conservation, that the total energy head at section A (
E
1
) must equal the total energy head
at section B (
E
2
), and using Equation 22.16 we get Bernoulli's equation:
2
2
P
w
V
P
w
V
AA
BB
z
++=++
z
(22.17)
A
B
2
g
2
g
The pipeline system shown in Figure 22.4 is horizontal; therefore, we can simplify Bernoulli's equa-
tion because
z
A
=
z
B
. Because they are equal, the elevation heads cancel out from both sides, leaving
Total energy line
2
2
v
B
/2
g
v
A
/2
g
Pressure
drop
P
A
/
w
P
B
/
w
E
1
E
2
Q
B
A
Constriction
z
B
z
A
Reference plane
FIGURE 22.4
The law of conservation: Because the velocity and kinetic energy of the water flowing in
the constricted section must increase, the potential energy will decrease. This is observed as a pressure drop
in the constriction. (Adapted from Nathanson, J.A.,
Basic Environmental Technology: Water Supply, Waste
Management, and Pollution Control
, 2nd ed., Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, 1997, p. 29.)





























Search WWH ::

Custom Search