Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
2
2
D
=× =
1ft
2
12-inch pipe:
A
π
3 14159
.
×
=
0.785 f
t
4
4
2
2
D
=× =
0.5 ft
96 ft
2
6-inch pipe:
A
π
3 14159
.
×
=
0.1
4
4
The continuity equation now becomes
2
2
0.785 ft
×
3ft/sec
=
0.196 ft
×
V
2
Solving for
V
2
,
2
0.785 ft 3ft/sec
0.196 ft
×
V
2
=
=
12 ft/sec or
fps
2
22.3.2 p
ressure
and
v
eloCity
In a closed pipe flowing full (under pressure), the pressure is indirectly related to the velocity of the
liquid. This principle, when combined with the principle discussed in the previous section, forms
the basis for several flow measurement devices (Venturi meters and rotameters), as well as the
injector used for dissolving chlorine into water and for dissolving chlorine, sulfur dioxide, or other
chemicals into wastewater:
Velocity
1
× Pressure
1
= Velocity
2
× Pressure
2
(22.15)
or
V
1
P
1
=
V
2
P
2
22.4 BERNOULLI'S THEOREM
Swiss physicist and mathematician Samuel Bernoulli developed the calculation for the total energy
relationship from point to point in a steady-state fluid system in the 1700s (Nathanson, 1997). Before
discussing Bernoulli's energy equation, it is important to understand the basic principle behind
Bernoulli's equation. Water (and any other hydraulic fluid) in a hydraulic system possesses two
types of energy—kinetic and potential.
Kinetic energy
is present when the water is in motion. The
faster the water moves, the more kinetic energy is used.
Potential energy
is a result of the water
pressure. The
total energy
of the water is the sum of the kinetic and potential energy. Bernoulli's
principle states that the total energy of the water (fluid) always remains constant; therefore, when
the water flow in a system increases, the pressure must decrease. When water starts to flow in a
hydraulic system, the pressure drops. When the flow stops, the pressure rises again. The pressure
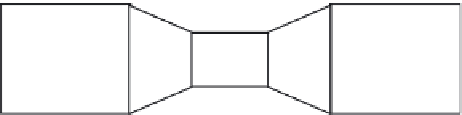
gauges shown in Figure 22.3 illustrate this balance more clearly.
FIGURE 22.3
Demonstration of Bernoulli's principle. (From Spellman, F.R. and Drinan, J.,
Water Hydraulics
,
Technomic, Lancaster, PA, 2001.)



















Search WWH ::

Custom Search