Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
processes of karst formation and evolution. But a
broader understanding of the contemporary Earth's
dynamics and its direct impact on the faulting and
fracturing of the rock volumes leads to the inevitable
conclusion that these two phenomena are final results
at different levels of the tectonic stresses. The
mechanism in the focus of every earthquake is an
informative source today about the regional (strong
earthquakes) and local (weaker earthquakes) tectonic
stress characteristics. It has been demonstrated in
Sect.
2.2.2
how the tectonic stresses control the
principal tendencies of the formation of the under-
ground karst systems of galleries. Furthermore, if the
karstified rocks are situated inside a tectonic province
with contemporary expressed activity, the earth-
quakes could be the factor for secondary moment
deformations of the speleosediments. This phenom-
is why some basic information on the mechanism of
formation of the dislocation in the earthquake focus,
and how it is recognized by ''the fault plane solution''
from
Fig. 2.17
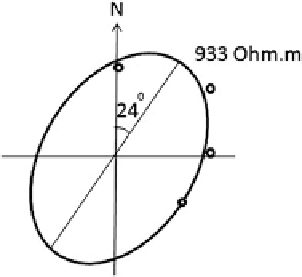
Ellipse of anisotropy of the apparent resistivity values
measured by array AB/2 = 25 m at 4 azimuths (Rumyantsevo,
North Bulgaria). Direction of the long axis of anisotropy—N 24;
Coefficient of anisotropy—1.29; Eccentricity—0.348
detected
at
depths
corresponding
to
arrays
AB/2
= 10 m and AB/2 = 25 m.
Lithological alternation is the possible reason for the
shallow level (AB/2 = 10 m), while for greater depth
(AB/2 = 25 m), this could reflect only the presence of
karst cavity elongated in NE-SW direction (Fig.
2.17
).
Dipole profiling in 65 points located in the area
using the scheme of Middle Gradients was applied
with 50 m spacing between the current electrodes
A and B. A map of apparent electric resistivity of the
southern part of the studied area has been compiled
(Fig.
2.18
). It is evident, that the discovered by Well
10 karstic cavity is reflected by the elongated toward
SW electrical anomaly with values higher then
850 Xm. But the very high resistivities in the northern
part of the studied area, probably related to near sur-
face limestone forming the third horizon of Kailaka
Formation, can mask any other existence of karst
structures below these layers. The high electrical
resistivity could be also related to karst structures in the
upper part of the section, but this can be verified only
by drilling. The practical conclusion is that the karst
cavity zone intersected by the well is probably devel-
oping as underground gallery in southwest direction. It
drains the system toward the open surface karst and
underground forms at the southwest of the studied area.
the
records
of
the
seismic
waves
will
be
presented.
Reid (
1911
) presented his theory about the ''elastic
rebound'' in his classic study on the dislocations
along the fault system San Andreas after the earth-
quake in San Francisco in 1906. Reid formulated five
principal statements in the theory (after Stacey
1972
),
as follows:
1. The rocks destruction causing tectonic earthquake
comes as a result of accumulation of elastic
deformation beyond the limit that rock can with-
stand. The deformation arises at relative move-
ment of neighboring blocks in the Earth's crust.
2. The relative displacement of the blocks is not
sudden at the moment of disruption, but it
increases gradually for a longer or shorter periods
of time.
3. The movement at the moment of earthquake con-
sists only of ''elastic rebound''—a sharp moving of
the fault' walls up to the position, where the elastic
deformations are missing. This movement is visual
only to a few miles far from the fault.
4. The seismic waves originate out of the fault sur-
face. First, the area of the surface where they arise
out is very small, but after that it increases fast and
becomes very large, but the velocity of its propa-
gation does not exceed the shear wave's velocity
of the rocks.
2.2.4
Earthquake Fault-Plane Solutions
The knowledge of the processes inside the earth-
quakes foci at first look is not evidently related to the