Database Reference
In-Depth Information
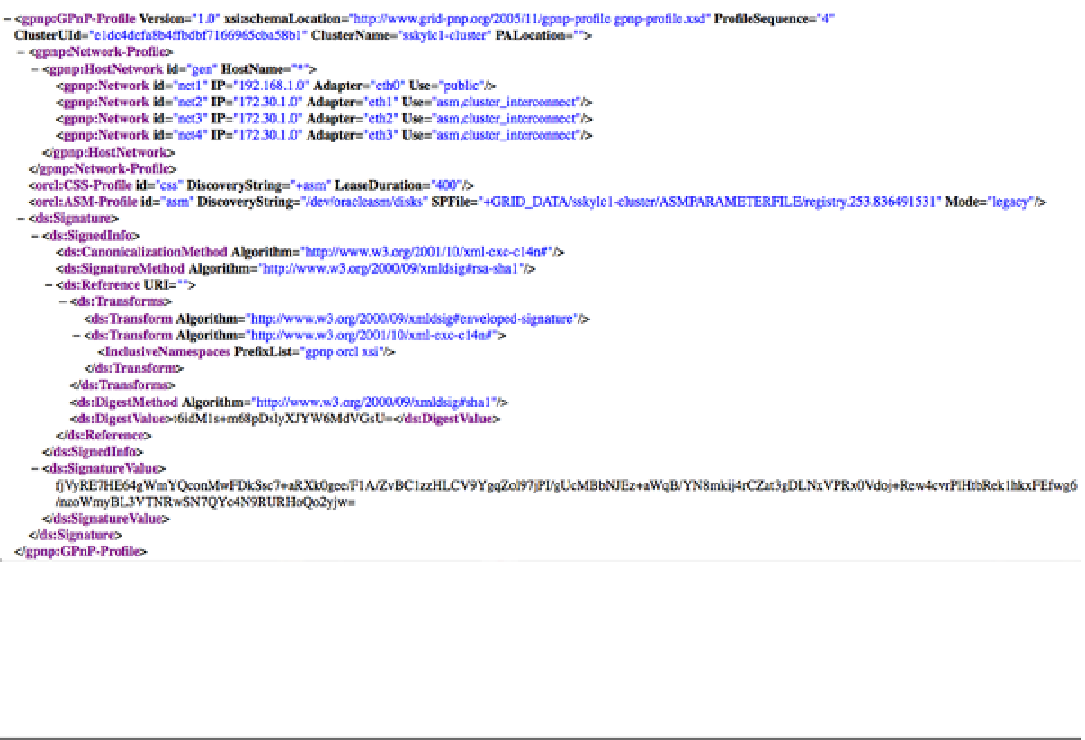
Figure 3-3.
GPnP profile with HAIP information
The HAIP resource is configured as under GPnP with the HAIP installation. Oracle configures an IP similar to the
virtual IP (VIP) for every NIC configured as private network.
■
to overcome some of the inbuilt flaws with the transmission Control protocol (tCp)/ip architecture, oracle had
introduced the database vip in oracle Database 10g release 1. in this case, a vip address was provided by the network
administrator and the same was added to the
/etc/hosts
file and subsequently mentioned as part of the clusterware
installation process.
Note
The VIP used for the private interconnect is not a predefined IP address by the network administrator. It's
automatically assigned from the IP addresses that are available from the “link local” block of addresses on all servers
in no specific order. The database configuration also inherits the interconnect information from the GPnP profile.
The number of High Availability IP (HAIP) addresses is decided by how many private network adapters are active
when OSW comes up on the first node in the cluster. If there's only one active private network, OSW will create one; if
two, OSW will create two; and if more than two, OSW will create four HAIPs. The number of HAIPs won't change even
if more private network adapters are activated later; a restart of clusterware on all nodes is required for new adapters
to become effective.
OSW automatically picks link local addresses from reserved 169.254.*.* subnet for HAIP, and it will not attempt
to use any 169.254.*.* address if it's already in use for another purpose. Using HAIP Interconnect traffic will be
load balanced across all active interconnect interfaces, and the corresponding HAIP address will be failed over
transparently to other adapters if one fails or becomes noncommunicative.
1
1
Metalink Note: 1210883.1, 11gR2 Grid Infrastructure Redundant Interconnect and ora.cluster_interconnect.haip

Search WWH ::

Custom Search