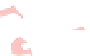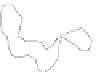Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
BA
RO
BA
RO
BA
RO
RO
BA
BA
BA
BA
BA
RO
RO
BA
BA
BA
BA
BA
BA
BA
YG
YG
YG
YG
YG
YG
YG
YG
YG
RO
RO
YG
YG
RO
YG
YG
YG
YG
MK
YG
RO
BG
RO
MK
YG
MK
YG
RO
RO
RO
BG
RO
RO
BG
RO
RO
RO
RO
RO
RO
RO
RO
RO
RO
RO
MK
MK
MK
BG
MK
AL
BG
MK
AL
BG
MK
AL
MK
MK
MK
RO
YG
YG
RO
YG
KS
KS
RO
KS
KS
KS
KS
AL
YG
YG
YG
AL
YG
YG
AL
YG
YG
YG
YG
AL
AL
AL
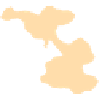
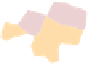
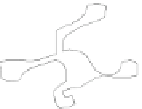
(a) MapSets
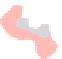
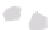
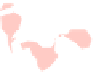
(b) GMap
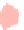
(c) BubbleSets
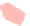
(d) KelpFusion
Fig. 7.
The graph of genetic similarities between 50 individuals in Europe. The layoutiscomputed
using the principal component analysis, while the clusters correspond to the countries of origin
of the individuals.
clustering is based on the political party they represent, red for republicans and bluefor
democrats. Clearly, both clustering and geographic information of the vertices are fixed
and cannot be changed. One can see that GMap produces fragmented clusters, while
BubbleSets and KelpFusion compute overlapping regions. On the other hand, the result
of MapSets is contiguous and non-overlapping, which makes it easier to analyze the
distribution of senators over the map.
The second example shows the population structure within Europe [17]. The origi-
nal points correspond to genetic data from 1
,
387 Europeans (but we sampled only 50
vertices corresponding to Eastern Europe for illustration purposes). The positions of the
vertices come from the original principal component analysis, based on the similarity
matrix. As the authors point out, the PCA plot (appropriately rotated) closely matches
the geographic outlines of Europe; hence, it is undesirable to change the node positions.
The clusters are extracted independently and corresponds to the countries of origin of
the individuals. Again, only MapSets constructs non-fragmented disjoint regions; see
Fig.7.Arguably, this is easier to analyze than the overlapping regions produced by
BubbleSets and KelpFusion.
We next analyze the performance of our ink minimization heuristic. To this end, we
utilize a collection of 9 real-world networks, that are embedded and clustered using the
GMap tool with the default setting.Table1gives details aboutthegraphs and mea-
surements of our ink saving algorithm. Here, ALG shows the ratio of the total ink of
the computed trees to the total length of the minimum spanning trees computed indi-
vidually for every cluster. In other words, this is an approximation factor achieved by
ouralgorithm on the test cases. Although we can only guarantee factor
kˁ
, in practice
the algorithm performs very well, always producing asolution at most 1
.
6 times worse
than the optimal. Our experiments indicate that ink minimization strategy often results
in aesthetically more pleasant map visualizations.
Similarly, ALG
fd
indicates the utilized ink after the force-directed adjustments. As
expected, the ink increases after the step, but the increase is not significant. On the other
hand, the adjustments improve the quality of the resulting regions.