Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
in Sasanishiki. However, if the slower binding reflected lowered affinity of Norin 1 for
dimers in DNA, the E-S complexes of Norin 1 might be less stable than those of
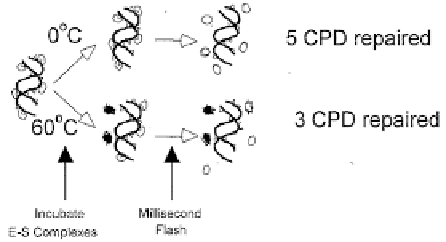
Sasanishiki. Complex stability can be probed by their thermal stability: E-S complexes
would be allowed to form, then challenged by incubation at a series of temperatures
before administration of a photoflash. Decreased E-S stability would be reflected by
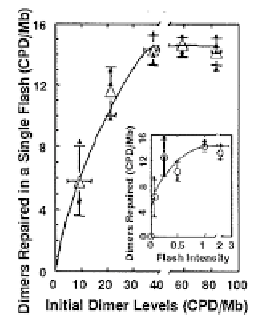
Figure 12. Measurement of photolase-dimer complex stability by photoflash analysis.
lower photorepair in the flash reaction, whereas unaltered E-S complex stability would
be reflected in similar properties of the complexes in both strains. However, since
artifacts could result from heating intact seedlings, it would be preferable to use extracts
of the plants.
First, it was necessary to determine whether the apparent photolyase
deficiency observed
in planta
was observed in extracts of the seedlings. They made
Figure 13. Photolyase deficiency in Norin 1 is observed in vivo and in vitro
extracts of seedlings of the two strains, and tested their photorepair activity
in vitro
, and
compared the results with those for dimer repair
in planta
. The results are shown in
Figure 13. The data show that extracts of Norin 1 seedlings also had lower photolyase
activity than did Sasanishiki, just as is observed in the intact plants.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search