Database Reference
In-Depth Information
0.85
0.96
w GPS context
w GPS context
0.95
0.8
0.94
0.93
0.75
original image
original image
alpha=5, beta=1
alpha=40, beta=10
cirm: dx=10, dy=10
cirm: dx=0.0001, dy=0.0001
alpha=5, beta=1
alpha=40, beta=10
cirm: dx=10, dy=10
cirm: dx=0.0001, dy=0.0001
0.92
0.7
0.91
3
5
6
9
10
12
3
5
6
9
10
12
Top
N
Top
N
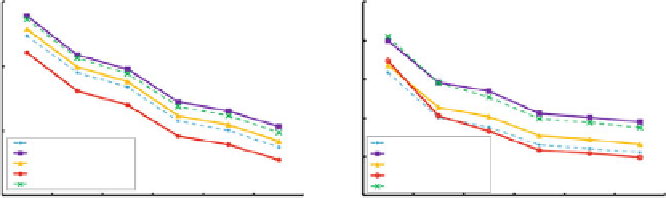
Fig. 4.15
, with
the conventional CBIR (original), as well as the CIRM algorithm with parameter
dX
and
dY
,with
GPS information
Comparison of image contextual-based recognition by various parameter
ʱ
and
ʲ
y
t
<
y
b
hold for this bounding box, such that the
tf
q
should be approaching the
value 0, the further
x
i
from the bounding box; while ideally close to value 1 when
the feature point is inside the bounding box.
y
i
<
ʴ
Y
are two tunable parameters
for finding the best performance of the bounding box. Detailed explanation of the
algorithm can be found in [
139
].
Figure
4.14
shows MAP and NDCG measurements, by comparing the Gaussian-
based contextual method with the CIRM model, as well as the CBIR method using
the original image. It appears that the proposed method with parameters
ʴ
X
and
ʱ
=
40 and
ʲ
=
10 outperformed both CIRM in its best result with parameter
dX
=
0
.
0001 and
dy
=
0
.
0001, and the CBIR result of the original image without using contextual
model.
Figure
4.15
depicts a similar comparison using the GPS context re-ranking.
Again, the proposed method outperformed the CIRM method and the CBIR
algorithms. However, the best performance of the CIRM model at
dX
=
0
.
0001 and
dY
=
0
.
0001 is close to the performance of the proposed contextual model at
ʱ
=
5
and
1. This result can be explained, such that, by adopting the GPS filtering,
the margin of various methods is reduced.
ʲ
=
4.4.2.4
Evaluation of Mobile Recommendations
For the recommendations, our method is to use the visual photo taken by users
as the starting point, and to provide recommendation lists based on text searches
associated with the recognized object. First, the object is identified and matched
to the database. Then, the matched metadata is used as a text query to do a text-
based search. The final result is then re-ranked by the relevant GPS distance from
the query's image location to the ranked list image locations.
The evaluation was conducted exclusively on a vertical domain of food cuisines.
A total of 306 photos were randomly picked and manually labeled and categorized
them into 30 featured themes of food dishes, such as beef, soup, burger, etc. A 300
Search WWH ::

Custom Search