Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 1
Blood cell variables
#
Variable
Type
Domain
1
Area
Ranged 163:1376
2
Convex area Ranged 187:1781
3
Perimeter
Ranged 58.97056:218.2082
4
Eccentricity
Ranged 0:0.965444268
5
Target
Binary
(1 for benign cell, 0 for distorted cell)
Apart from the NN, the recursive binary C&R tree has been applied to the term of regression
because all variables contain numeric values, as shown in
Table 1
. In this table, all variables
range in type, and only the output (target) variable has binary values (e.g., 1 for benign cells
and 0 for distorted cells). The binary tree is divided into two branches based on the Gini index
and recursively trained with a maximum tree depth of five levels, and it stops when it achieves
a parent branch minimum of 2% and a child branch minimum of 1%.
Finally, the performance of each classification model is evaluated using three statistical
measures: classification accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity. These measures are defined as
true positive (TP), true negative (TN), false positive (FP), and false negative (FN). A TP de-
cision occurs when the positive prediction of the classifier coincides with a positive prediction
of the previous segmentation. A TN decision occurs when both the classifier and the segment-
ation suggest the absence of a positive prediction. An FP occurs when the system labels the
benign cell (positive prediction) as a malignant or distorted one. Finally, An FN occurs when
the system labels a negative (malignant) cell as positive. Moreover, the classification accuracy
is defined as the ratio of the number of correctly classified cells to the total number of cells,
and it is equal to the sum of TP and TN divided by the total number of RBCs (
N
), as shown in
(6)
Sensitivity refers to the rate of correctly classified positives, and it is equal to TP divided by
the sum of TP and FN.










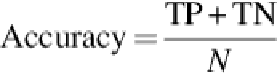

Search WWH ::

Custom Search