Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
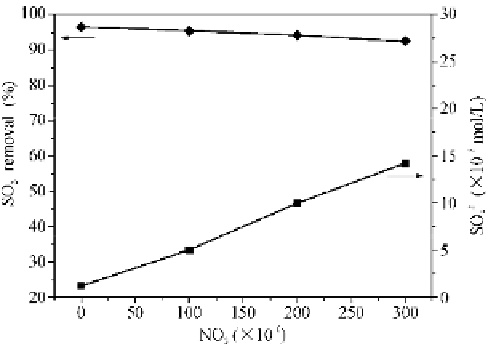
4.5.2 Effect of NO
2
on SO
2
Removal
Under the same liquid conditions as those in Fig. 4.11, the experimentally-
determined NO
2
influence on the SO
2
removal and product concentration is
presented in Fig. 4.13. The SO
2
removal efficiency slightly decreases from 96.5%
to 92.6% as the NO
2
concentration increases from 0 to 300 ppm. The nitrous and
nitric acid generation, produced through the reactions in Eqs. (4.4), (4.10), and
(4.11) when NO
2
enters the liquid phase, increases the H
+
concentration and
decreases the pH value. Under flue gas conditions where the NO
x
concentration is
clearly smaller than that of SO
2
, the influence of the NO
2
adsorption on the H
+
concentration and pH value is weak, finally resulting in a slight decrease in the
SO
2
removal with the NO
2
concentration. However, the change of SO
4
2
concentration is noticeable in Fig. 4.13. It should be noted that a 1.2×10
5
mol/L
SO
4
2
concentration appears under the circumstances without NO
2
. An explanation
may lies in the potential oxidation of tetravalent-S components through the
oxygen dissolved in the solution. With increasing NO
2
, reactions between NO
2
and
tetravalent-S components occur, resulting in an apparent increase in the SO
4
2
concentration (reaching 1.42×10
4
mol/L at 300 ppm NO
2
). In practical
desulfurizer's operations, it is accepted that the NO
2
existence is beneficial to the
change in SO
2
and can increase the plaster output.
(ppm)
Fig. 4.13
Influence of NO
2
on SO
2
removal and absorption product
Search WWH ::

Custom Search