Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
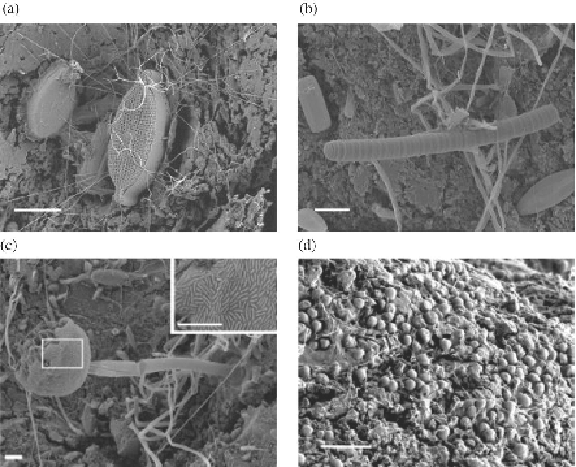
Figure 6.16
Electron micrographs (a-c) showing the diversity of
microbial flora on polyolefin debris surfaces exposed to marine
environments. Micrograph (d) shows pitting around the microbes. All
scale
bars
are 10 µm.
Source: Reprinted with permission from Zettler ER, Mincer TJ, Amaral-Zettler
LA. Life in the “plastisphere”: microbial communities on plastic marine debris.
Environ Sci Technol 2013;47 (13):7137-7146. Copyright (2003) American
Chemical Society.
PE is known to undergo biodegradation by numerous microorganisms: a
recent review (Restrepo-Flórez et al., 2014) lists 17 genera of bacteria and
11 genera of fungi that biodegrade PE. These include
Rhodococcus ruber
C-208 that secretes a laccase enzyme (Santo et al., 2013) well known to
degrade lignins (Coll et al., 1993). In the study of Sivan et al. (2006),
cell-free laccase enzymes catalyzed by copper were able to reduce the
Mn
(g/mol) of PE by 15-20%. Incubating the plastic in a laboratory culture
of live cells can also lead to significant degradation. Reduction of
Mw
(g/
mol) by up to 25% was reported (Hadad et al., 2005) in PE films incubated
with the thermophilic bacterium
Brevibacillus borstelensis
. Many other