Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
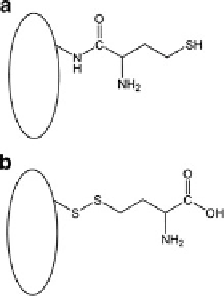
Fig. 4.2 Schematic structures of N-Hcy-protein and S-Hcy-protein adducts. (a) N-Hcy-protein:
the carboxyl group of Hcy forms an amide bond with the side chain amino group of a protein lysine
residue (Lys525 in human serum albumin). (b) S-Hcy-protein: the thiol of Hcy forms a disulfide
bond with the side chain thiol of a protein cysteine residue (Cys34 in human serum albumin). The
ovals represent protein molecules (Reproduced from [81])
These findings demonstrate that Hcy-thiolactone undergoes two major reactions
in serum: (1) protein N-homocysteinylation and (2) enzymatic hydrolysis to Hcy,
followed by protein S-homocysteinylation. The enzymatic hydrolysis to Hcy is
catalyzed by serum Hcy-thiolactonase/PON1 [81]. Structures of N-Hcy-protein and
S-Hcy-protein adducts are illustrated in Fig.
4.2a, b
, respectively.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search