Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
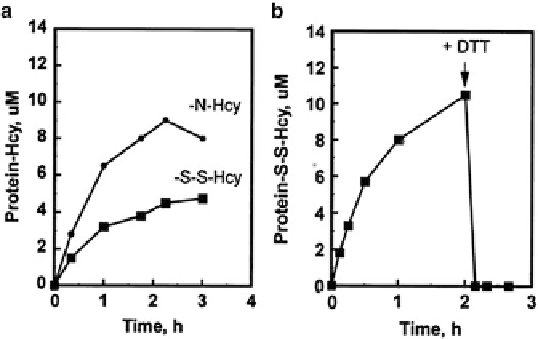
Fig. 4.1 Reactions of Hcy-thiolactone and Hcy in human serum. (a) Kinetics of protein
N-homocysteinylation (filled circles) and protein S-homocysteinylation (filled squares) in the
presence of 12
M[
35
S]Hcy-thiolactone. (b) Kinetics of protein S-homocysteinylation (filled
μ
M[
35
S]Hcy. At the point indicated by an arrow, 10 mm DTT was added
(Reproduced from [81])
squares) with 12
μ
increasing Hcy concentration (Fig.
3.7
) and decreases with increasing levels of
folic acid (which lowers Hcy levels) and HDL (which hydrolyzes Hcy-thiolactone)
(Table
3.9
) [74].
Subsequent studies have revealed that the incubation of human serum with
[
35
S]Hcy-thiolactone results in a progressive incorporation of the [
35
S] radiolabel
into protein (Fig.
4.1a
). At 3 h, most of the [
35
S] becomes protein bound and is
precipitable by trichloroacetic acid. Treatment with dithiothreitol (DTT) of the
[
35
S]Hcy-thiolactone-modified serum protein releases only
30 % of the
incorporated [
35
S] as free [
35
S]Hcy, which suggests two modes of Hcy binding
to protein [78, 81]. [
35
S]Hcy in the DTT-resistant fraction of the [
35
S]-protein
adducts is bound to a side chain amino groups of protein lysine residues [78, 96].
Similar fractions of N-[
35
S]Hcy-protein and S-[
35
S]Hcy-protein adducts are
obtained with [
35
S]Hcy-thiolactone concentrations ranging from 10 nM to 1 mM
[78].
Control experiments, with separately prepared S-[
35
S]Hcy-protein, confirm
that DTT treatment releases all disulfide-bound Hcy from the protein.
For example, incubation of exogenous [
35
S]Hcy with human serum results in a
progressive formation of S-[
35
S]Hcy-protein adducts that are precipitable with
trichloroacetic acid. The treatment with DTT renders essentially all [
35
S]Hcy
from the S-[
35
S]Hcy-protein adducts trichloroacetic acid soluble (Fig.
4.1b
).
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under nonreducing conditions demonstrates
that S-[
35
S]Hcy-albumin represents most (
95 %) of S-[
35
S]Hcy-protein in
>
human serum [81].
Search WWH ::

Custom Search