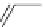Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 5
4-
tert
-Butyl-1,5,8-
trimethyl- and 4-isopropyl-
1,5,8-trimethylphenanthrene
[
27
-
29
]
12
13
O
S
S
O
O
S
Al/Hg
O
O
O
O
S
S
14
16
,69%
15
, 67%
S
O
O
S
8
Ni
NaOH
O
O
O
O
S
18
,34%
17
Scheme 3
Synthesis of 4,5-diethylphenanthrene
18
[
30
]
Dianions of 4,5-dialkylphenanthrenes are stable and maintain their helicity [
28
,
29
].
The dynamic NMR studies of
13
indicate that the activation barrier of racemization
decreases substantially from 22.2 kcal/mol at 114
C to 15.4 kcal/mol at 46
Cof
its dianion (
13
2
/2Li
+
). The lower activation barrier has been attributed to the
elongation of the C9-C10 bond in the dianion.
A synthetic pathway for the 4,5-diethylphenanthrene derivative
18
was also
reported (Scheme
3
)[
30
]. Pinacolic reduction of
14
produced
15
, which in turn
underwent a Diels-Alder reaction with maleic anhydride to give
16
. Aromatization
followed by desulfurization then afforded
18
bearing the ethyl groups at the C4 and
C5 positions.
2.2
4,5-Diarylphenanthrenes
Photocyclization of 1-buten-3-yne
19
provided an efficient synthetic pathway to 4,5-
diphenylphenanthrene (
20
)(Scheme
4
)[
31
,
32
]. Similarly, 4,5-diphenyl- (
21
),
4-(3,5-dimethylphenyl)-5-phenyl- (
22
), and 4,5-bi(3,5-dimethylphenyl)triphenylene
(
23
)(Fig.
6
) were also synthesized from the corresponding 1-buten-3-ynes [
33
].
Monobromination of
22
and
23
produced
24
and
25
, respectively.
Variable-temperature NMR studies of the NMR signals of the methyl groups of
the 3,5-dimethylphenyl substituents in
22
and
23
provided the rotation barriers