Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 4.8 Sequences alignment of nuclear miRNAs with c-Myc and Engrailed genes (
http://
mirdborg/miRDB/
;
http://mirnamapmbcnctuedutw/
; Raver-Shapira et al.
2007
)
Table 4.9 Comparison between cellular oxygen consumption of mammals (Hainaut and
Hollstein
2000
)
V
O2max
/
M
(ml.s
1
.kg
1
)
V
/
M
(ml/kg)
Dog
2.29
40.6
Goat
0.95
13.8
Horse
2.23
30.0
Steer
0.85
11.6
Table 4.10 Number of common subsequences of lengths 6 and 7 between the mitochondrial
tRNA loops and the noncoding mitochondrial genomes of bos (total length 8,493 bases) and equus
(total length 4,535 bases) (
http://megasunbchumontrealca/ogmp/projects/other/cp_list.html
)
Subsequences Observed bos Expected bos
Observed equus Expected equus
TACCAC
2
2
0
1
TACCAT
1
2
0
1
ACCGTT
2
2
0
1
ACCATT
1
2
0
1
CTTGAA
1
2
0
1
ATTTGAA
1
0.5
0
0.25
Total
8
10.5
6.5 (
m
2
σ
)
0
5.25
4.6 (
m
2
σ
)
4.5 Global Influence of microRNAs
4.5.1 Physiological Role in Cell Energetics
The unspecific inhibitory noise from the microRNAs has a global resultant on the
intermediary metabolism in, e.g., higher mammals. Their role is essential in the
brake/acceleration balance of the network dynamics preventing artificial attractors
to be expressed, which could lead either to pathologic rhythms, or to steady states
with too high concentrations of certain metabolites.
Following the comparative physiology study about cell consumption of oxygen
by mammals done in (Weibel et al.
1991
), let us consider
V
, the total mitochondrial
volume of muscle and
V
O2max
, the O
2
consumption rate per unit mass of whole body
mass
M
of the mitochondria of these mammals. Table
4.9
shows that nonruminant



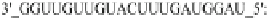


































Search WWH ::

Custom Search