Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
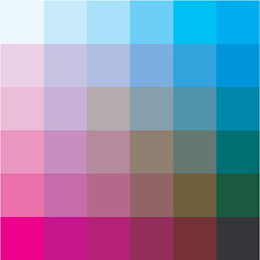
In a subtractive color model, such as that which defines ink mixtures for printing
shown above, successive layers of ink result in darker, more saturated colors, to a
point. Once the ink layers no longer permit a substantial amount of light to reflect
from the printed surface, the combined colors become less saturated and eventually
neutral and black. Subtractive color is also altered by the chemical makeup of the pig-
ments used to color the inks.
Hue Relationships
Designers can create interaction between different hues, independ-
ent of their saturation or value, according to where they lie on the color wheel. The
closer together the colors appear on the wheel, the more similar their optical qualities
and, hence, the more harmonious or related. The further apart colors are on the wheel,
the more their optical qualities contrast.