Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
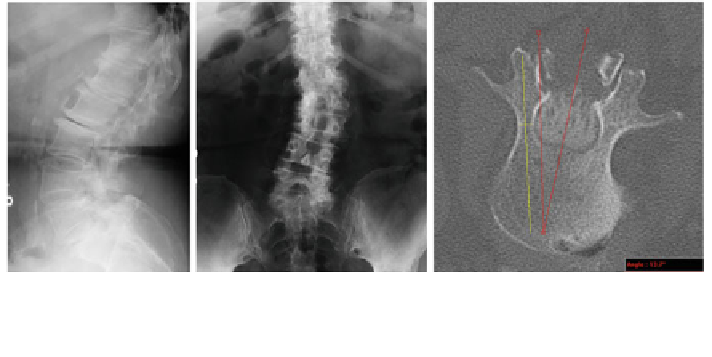
Fig. 1 On the left and middle panels, bi-planar radiographs are shown. Radiographs are
sometimes used in planning spine surgeries with complex patient morphology. On the right,an
axial image from a CT scan is shown with distance and angle measurement lines superimposed
3 Procedure Planning Work
fl
ow
3.1 Traditional Planning
Traditional methods of planning for corrective spinal surgery include the use of 2D
images from radiographs or from axial, sagittal and coronal views of CT or MRI
exams. Linear and angular measurements are made with simple tools from within
image viewing programs, or directly on
film using markers, cutouts and rulers.
Figure
1
shows a typical pair of radiographs and CT slice which would be used in
the planning of a procedure. For this study, only CT data was used for planning as it
provides more detail than a radiograph. During the planning process, the axial images
are reviewed and critical vertebrae are identi
ed. The length of the vertebra is
measured (using a graphic line measurement tool) from the pedicles to the anterior
surface of the vertebral body. In addition, the width of the bone at the narrowest point
of the pedicle is measure in order to select screws which will not penetrate into the
spinal column. The angle of approach is determined by an estimated deviation from
the spinous process. Consistent with current clinical practice, the proposed screws
and angles of insertion are documented, by hand, on a planning form.
3.2 Templating-Based Procedure Planning
3.2.1 Pre-operative Imaging
The SSP application runs on a standard desktop computer. The software can import
data either directly from the
file system or through an institutional PACS in the
form of a high resolution CT scan acquired with standard imaging protocols.