Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
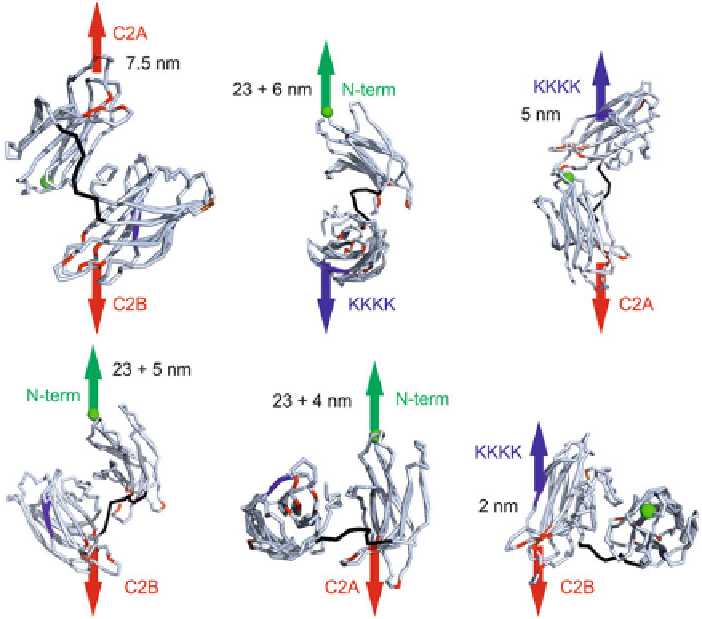
length that synaptotagmin-1 can connect two membranes and are determined by
the interconnecting linker and the surface interactions between the C2-domains.
These distances are overestimates, because membrane insertion and bending are not
accounted for. The distance from the polybasic patch to the transmembrane helix is
∼
23nm linker). However, the distance synaptotagmin-1 teth-
ers liposomes without
Ca
2
+
28nm (including the
∼
is likely shorter since the debye length is only
∼
25Å,
but higher than the
5nm from the FRET experiments. The maximum distances
the
Ca
2
+
-bound C2AB-domain could span two membranes is
∼
2-7.5nm, close to
the 4nm from cryo-electron microscopy data [
9
]. These distances would explain
why decreasing the ionic strength and increasing the sebye length from
∼
7to25Å
has such a dramatic effect on membrane fusion. Thus, at low ionic strength,
Ca
2
+
∼
Fig. 3.13
Molecular dynamic simulations to estimate the maximal distances between the various
domains. In the simulations, we pulled pair-wise on various membrane binding sites of the C2AB-
domain: the N-terminus (
green
), the polybasic lysine patch (
blue
; KKKK) and the
Ca
2
+
-binding
sites of the C2A- and C2B-domain (
red
). The two conserved arginines (R398 and R388) are shown
in
brown
; the linker is in
black
. The N-terminus is connected to the transmembrane helix with a 61
residue linker that can extent to
23nm. Maximal distances are indicated in the figure; these are an
approximate for the tethering distances of the membranes, but do not take into account additional
interactions such as membrane insertion and bending
∼