Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
complete path has to be established prior to the start of communication between a
source and a destination. The established path will remain in existence during the
whole communication period. In a packet switching mechanism, communication
between a source and destination takes place via messages that are divided into
smaller entities, called packets. On their way to the destination, packets can be
sent from one node to another in a store-and-forward manner until they reach
their destination. While packet switching tends to use the network resources more
efficiently, compared to circuit switching, it suffers from variable packet delays.
11.5.4. Topology
According to their topology, INs are classified as static versus dynamic networks. In
dynamic networks, connections among inputs and outputs are made using switching
elements. Depending on the switch settings, different interconnections can be estab-
lished. In static networks, direct fixed paths exist between nodes. There are no
switching elements (nodes) in static networks.
Having introduced the general criteria for classification of interconnection net-
works, we can now introduce a possible taxonomy for INs that is based on topology.
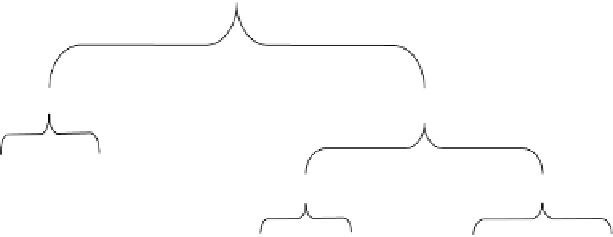
In Figure 11.12, we provide such a taxonomy.
According to the shown taxonomy, INs are classified as either static or dynamic.
Static networks can be further classified according to their interconnection patterns
as one-dimension (1D), two-dimension (2D), or hypercubes (HCs). Dynamic net-
works, on the other hand, can be further classified according to the scheme of inter-
connection as bus-based versus switch-based. Bus-based INs are classified as single
bus or multiple bus. Switch-based dynamic networks can be further classified
according to the structure of the interconnection network as single-stage (SS), multi-
stage (MS), or crossbar networks.
Multiprocessor interconnection networks are explained in detail in Chapter 2
of our topic on Advanced Computer Architecture and Parallel Processing
(see reference list).
Interconnection Networks
Static
Dynamic
1D
2D
HC
Bus-based
Switch-based
Single
Multiple
SS
MS
Crossbar
Figure 11.12 A topology-based taxonomy for interconnection networks
Search WWH ::

Custom Search