Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
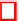
Algorithm 4.
DOOM ISD algorithm
For any fixed values of
n
,
r
and
w
, the following algorithm uses four parameters:
two integers
p>
0and
>
0andtwosets
W
1
⊂S
k
+
(
0
,p
1
)and
W
2
⊂S
k
+
(
0
,p
2
)
where
p
1
and
p
2
are positive integers such that
p
1
+
p
2
=
p
.
procedure
main doom
input
:
H
0
∈{
0
,
1
}
r×n
,
S
0
⊂{
0
,
1
}
r
repeat
P ←
random
n × n
permutation matrix
(
H
,H
,U
)
(doom 0)
←
PartialGaussElim(
H
0
P
)
// as in (1)
S←{s
0
U
T
| s
0
∈S
0
}
e ←
doom loop(
H
,H
, S
)
while
e
= fail l
return
(
P,e
)
procedure
doom loop
input
:
H
∈{
0
,
1
}
×
(
k
+
)
,
H
∈{
0
,
1
}
(
r−
)
×
(
k
+
)
,
S⊂{
0
,
1
}
r
for all
e
1
∈ W
1
(doom 1)
i ← e
1
H
T
,
s
1
← e
1
H
T
write(
e
1
,s
1
,i
)
// stores (
e
1
,s
1
)atindex
i
for all
e
2
∈ W
2
for all
s
=(
s
,s
)
∈S
(doom 2)
i ← s
+
e
2
H
T
,
s
2
← s
+
e
2
H
T
Elts
←
read(
i
) // extracts the elements stored at index
i
for all
(
e
1
,s
1
)
∈
Elts
(doom 3)
if
wt (
s
1
+
s
2
)=
w − p
return
e
1
+
e
2
(success)
return
fai l
(fail) l)
about
Nr/
log
2
N
column operations. For the extremal values of
N
of
5.3 (the
case most favorable to the attacker), assuming
K
1
=
K
2
=
K
3
/
2=1,wehave
P
n
(
p,
)=1andacomplexity
§
≈ Nr/
log
2
N
+2
+2
with
N
=2
2
/
k
+
≤
2
.
p
Unless we precisely use the optimal value of
p
, for which
N ≈
k
+
p
≈
2
,the
ratio
N/
2
will be significantly smaller than 1 and
K
0
= 0 provides an accurate
estimate. Finally when
p
minimizes the formula for the cost (this value, by
the way, is not necessarily an integer and does not correspond to a practical
implementation) we have a complexity of the form 2
(
r/
+ 4) and we cannot
neglect
r/
compared with 4. For the sake of simplicity, we do it nevertheless.
5.2 Complexity Gain from Multiple Instances
We will denote
WF
(
N
)
ISD
(
n,r,w
)=min
p,
T
N
(
p,
)