Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
60
60
50
50
40
40
30
30
20
20
10
0
10
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
A
B
Stimulation frequency, Hertz
Stimulation frequency, Hertz
50
2.3
2.2
40
2.1
30
2
1.9
20
1.8
10
1.7
1.6
0
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
2.2
2.4
2.6
2.8
3
D
C
Stimulation frequency, Hertz
Fractal dimension,
D
f1
50
80
70
40
60
30
50
40
20
30
10
20
0
10
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
2.2
2.4
2.6
2.8
3
F
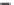
Figure 9.8
(a) Increase in the binding rate coefficient, k
1
with an increase in the stimulation frequency (in Hz).
(b) Increase in the binding rate coefficient, k
2
with an increase in the stimulation frequency (in Hz).
(c) Increase in the fractal dimension, D
f1
with an increase in the stimulation frequency in (Hz).
(d) Increase in the binding rate coefficient, k
1
with an increase in the fractal dimension, D
f1
.
(e) Increase in the binding rate coefficient, k
2
with an increase in the fractal dimension, D
f2
.
(f) Increase in the dissociation rate coefficient, k
d
with an increase in the stimulation frequency
(in Hz).
Stimulation frequency, Hertz
E
Fractal dimension,
D
f2
continued