Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
and physiological processes. High TNF concentrations in serum have been observed in path-
ological states such as endotoxic shock, graft rejection, HIV infection, and rheumatoid arthri-
tis (
De Kossodo et al., 1995
).
Wang et al. (2006)
assert that the electrochemical technique is
an attractive method for the immunoassay of biomarkers, especially since TNF-
a
, in general,
is observed to be at very low levels in biological samples such as serum.
Wang et al. (2006)
report that the electrochemical immunoassay technique is highly sensitive
and inherently simple. Furthermore, it can be miniaturized and is a low cost technique. These
authors further state that the inclusion of NPs in electrochemical sensors exhibits a significant
potential for the detection of trace biomolecules (
Daniel and Astruc, 2004; Wang et al.,
2004
).
Wang et al. (2006)
have developed and used poly(guanine)(poly[G]-)-functionalized
silica NPs along with mediator-induced catalytic oxidation of guanine for the amplified elec-
trochemical immunoassay of TNF-
a
.
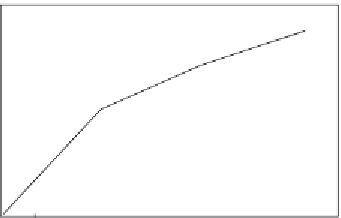
Figure 8.1
shows the binding of 1.0 ng/mL of TNF-
a
in solution to the poly(guanine)-
functionalized silica NPs (
Wang et al., 2006
). A single-fractal analysis is adequate to describe
the binding kinetics. These authors report that at 45 min incubation time the interaction of
TNF-
a
in solution and the TNF-
a
antibody immobilized on the electrochemical sensor
reaches saturation. The value of the binding rate coefficient,
k
, and the fractal dimension,
D
f
, for a single-fractal analysis are given in
Table 8.1
.
Zeng et al. (2006)
report that recently there has been an increasing demand to improve
the sensitivity and reaction rate parameters for both automated and miniaturized clinical anal-
ysis. These authors have very recently developed a quartz-crystal microbalance-based
25
20
15
10
5
0
0
10
20
Time (min)
30
40
50
Figure 8.1
Binding of 1.0 ng/mL of TNF-
(tumor necrosis factor) in solution to the poly(guanine)-
functionalized silica nanoparticles (NPs) (
Wang et al., 2006
).
a