Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
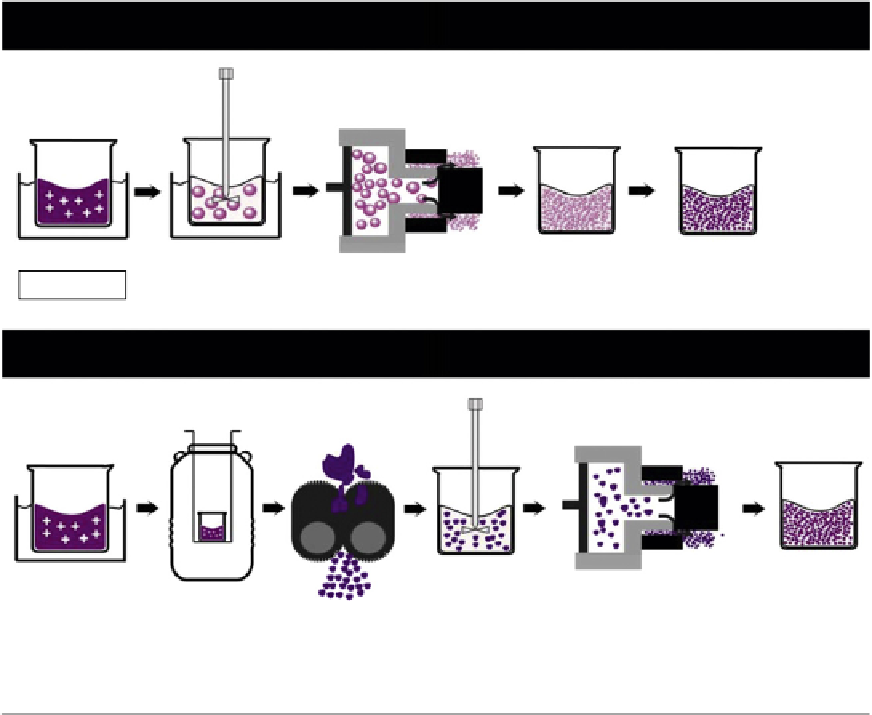
High-pressure homogenization - hot technique
SLNs
Pre-emulsion in a hot
aqueous surfactant
mixture
High-pressure homogenization
at a temperatue above the
lipids melting point
Solidification by
cooling down to
room temperature
Melting
lipids and drug
Hot o/w
nanoemulsion
High-pressure homogenization - cold technique
SLNs
Dispersing the
powder in an
aqueous surfactant
dispersion medium
Melting
lipids and drug
Solidification in liquid
nitrogen or dry ice
Grinding in a
powder mill
High-pressure homogenization at
room temperatue or below
FIGURE 23.5
Modalities used to prepare solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) by HPH.
23.3
Dental applications of nanoparticles
Nanoparticles have been proposed as drug-delivery systems for caries control and restoration, tooth
remineralization, management of dentinal hypersensivity, dental caries vaccine, oral biofilm man-
agement, root canal disinfection, local anesthesia, and periodontal infection. For example, nanoparti-
cles can be used to improve treatments for diseases of dental and oral structures using the classical
drugs. It is proposed that nanoparticles can be selectively delivered to target sites or cells. One of the
most important applications of nanoparticles in dentistry is the treatment of periodontal disease.
Periodontal disease is a collective term that includes several pathological conditions character-
ized by degeneration and inflammation of the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth: gum tis-
sue (gingiva), periodontal
57]
.The
relationship between the subgingival plaque and the development of periodontal disease is well
established. This infectious process shows different grades of severity: (i) gingivitis, the early phase
ligament, alveolar bone, and dental cementum
[7,8,53