Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
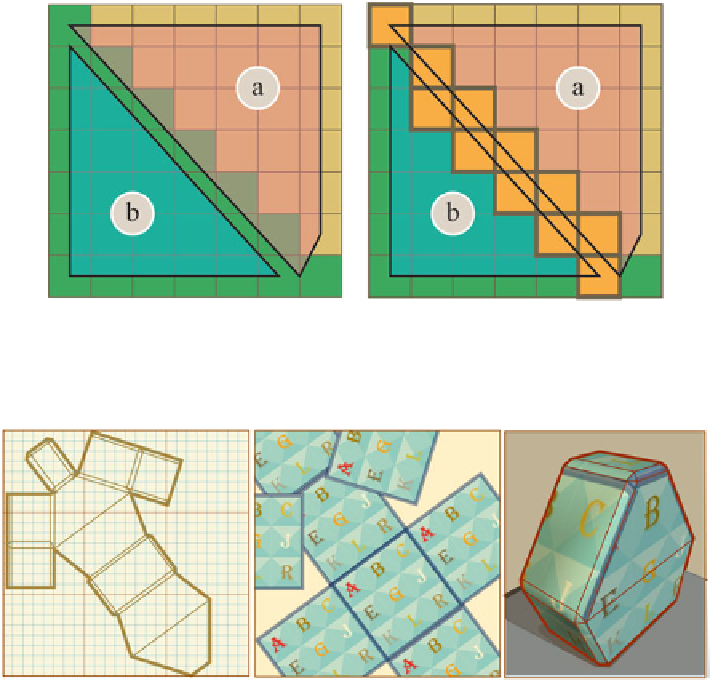
Fig. 10.37
Polygons
a
and
b
are less than a pixel away from each other, as shown by the high-
lighted
orange pixels
they share. Because of their proximity, their edges cannot be painted
separately
Fig. 10.38
This UV mapping solution is effi cient but it requires the map to be rotated on its axis
to align properly with the object it belongs to
10.6.4
Grouping and UVs
If different objects use the same material, their UVs will occupy the same space
(Fig.
10.40
). This is acceptable if one texture map is appropriate for them all. If not,
they should be assigned to different materials. One way to organize a large number
of parts is by material type, like wood, rubber, cloth, steel, etc. Most often, you will
have fewer parts than you have materials, so some parts will share the same mate-
rial. This is already an improvement over having everything assigned to the same
material, and is usually workable. On some occasions, your parts will be so complex
that you will want to keep your objects separate while texturing them. When that
is true, you may want to create temporary shaders, to keep the UVs separate while you
work with them, and then combine them when you are done.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search