Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
5
'
3
'
Target
sequence
Genomic DNA
3
'
5
'
5
'
3
'
1
Denaturation:
Heat briefiy
to separate DNA
strands
3
'
5
'
2
Annealing:
Cool to allow
primers to form
hydrogen bond
with ends of
target sequence
Cycle 1
yields
2
molecules
Primers
3
Extension:
DNA polymerase
adds nucleotides to
the 3
'
end of each
primer
New
nucleo-
tides
Cycle 2
yields
4
molecules
Cycle 3
yields 8
molecules:
2 molecules
(in white boxes)
match target
sequence
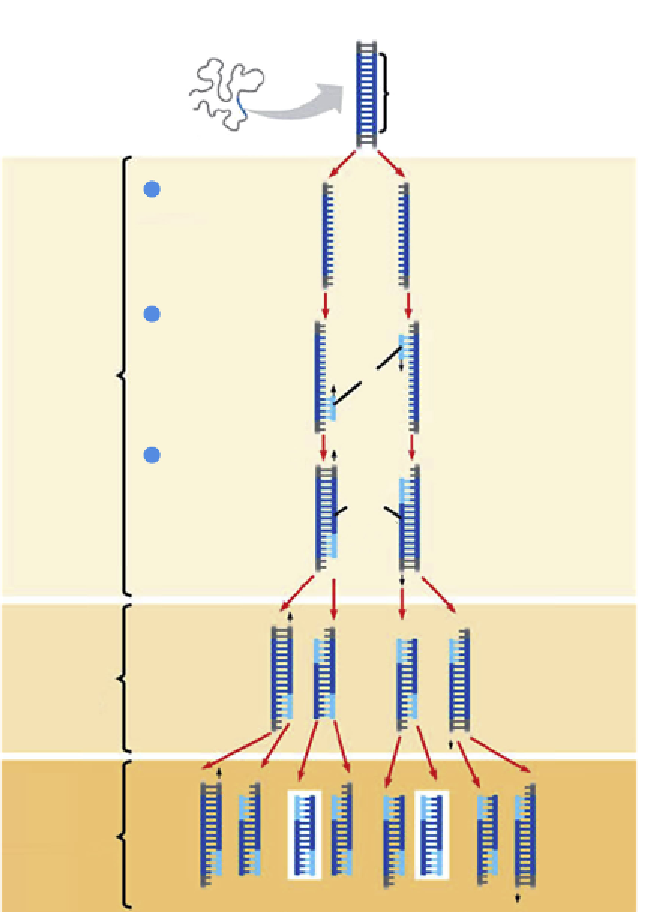
Figure 8.6
A schematic of the polymerase chain reaction. Amplification of a region
of DNA is accomplished by designing two primes that are complementary to the
sequence flanking the target region. A heat stable polymerase extends the primers
and produces copy of the target region. The dsDNA copy is denatured and synthesized
once more. This cycle is repeated many times (often 30 cycles), which produces many
copies of the target which can be detected. Source:
http://www.foodsafetywatch.
com/public/1050.cfm
.
(For color version of this figure, the reader is referred to the
online version of this topic.)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search