Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
adsorption quantities of LFA1 with 17.51% carbon and LFA2 with 39.87% carbon
were similar, and these values were larger than that of FA with 6.13% carbon. The
adsorption ability of fly ash was not proportional to its carbon content. Other ele-
ments in fly ash and the composition of flue gas might have great effects on mercury
adsorption by fly ash.
5.3.1.2 Hg
0
Adsorption Ability of Calcium-Based Sorbent
Three different sorbents, namely hydrated lime (Ca(OH)
2
of 97.6%), lime (CaO of
87.6%) and MFC (mixture of fly ash and lime), were chosen in the study of the Hg
0
adsorption ability of calcium-based sorbents.
Hg
0
adsorption ability of hydrated lime
Adsorption experiments were conducted on two kinds of simulated flue gas: 1) BL
and 2) BL added with 800 ppm SO
2
. Other conditions were the same (Hg
0
concen-
tration: 19.9 g/m
3
; temperature: 125 °C; flow: 1 L/min). The adsorption kinetic
and adsorption efficiency curves of Hg
0
by hydrated lime on the two kinds of
simulated flue gas are shown in Fig. 5.3. The existence of SO
2
was favorable for
hydrated lime adsorbing Hg
0
because SO
2
reacted with the hydrated lime, promot-
ing the adsorption of Hg
0
. Reaction equations are as follows:
, (5-1)
Ca(OH) +SO +O
CaSO +H O+O
2
2
2
4
2
2Hg +O
0
Hg O
, (5-2)
2
0
, (5-3)
Ca(OH)+SO+O+2Hg
CaSO+HO+HgO
2
2
2
4
2
2
. (5-4)
Ca(OH) +SO
CaSO +H O
2
2
3
2
0.6
no SO
2
800 ppm SO
2
100
0.5
0.4
90
Inlet Hg
0
20.5383
g/m
3
0.3
80
0.2
BL
800 ppm SO
2
Inlet Hg
0
19.8728
g/m
3
70
0.1
0.0
60
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
Time
(min)
Time (min)
(a) (b)
Fig. 5.3
Hg
0
adsorption by hydrated lime on two kinds of simulated flue gas
Hg
0
adsorption ability of lime
Adsorption experiments were conducted on two kinds of simulated flue gas: 1) BL
and 2) BL added with 800 ppm SO
2
. Other conditions were the same (Hg
0
concen-
tration: 18.4 g/m
3
; temperature: 125 °C; flow: 1 L/min). The adsorption kinetic and

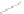

























































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search