Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Therefore, these four frame formats can reside on the same segment. A few differences exist,
which are explained.
The four frame formats are as follows:
•
Ethernet version 2
•
Novell 802.3 Raw
•
IEEE 802.3
•
IEEE 802.3 Subnetwork Access Protocol (SNAP)
Ethernet Version 2 Frame Format
Figure 4-2 shows the Ethernet version 2 frame format. The frame fields are described in
Table 4-1.
Ethernet V2 Frame Format
Figure 4-2
Preamble
8 bytes
DA
6 bytes
SA
6 bytes
Type
2 bytes
Data + pad
46-1500 bytes
FCS
4 bytes
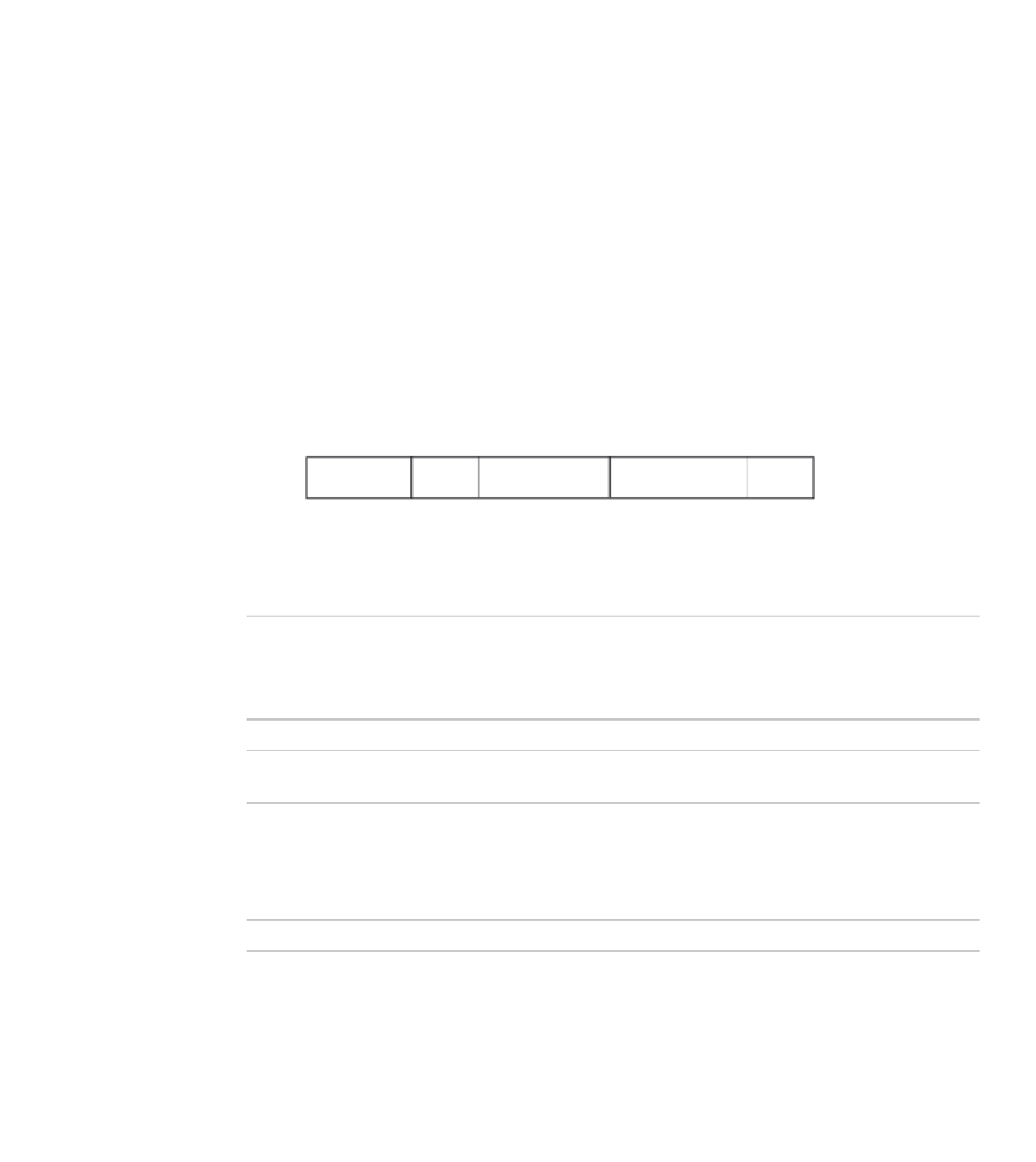
Ethernet V2 Frame Fields Descriptions
Table 4-1
Field
Description
Preamble
String of binary 1s and 0s ending with 11 to indicate the beginning of
the destination address (DA) field:
10101010 10101010 10101010 10101010 10101010 10101010
10101010 10101011
Destination Address (DA)
48-bit MAC layer Ethernet address of the destination host.
Source Address (SA)
48-bit MAC layer Ethernet address of the host that sent the frame
(source host).
Type
Contains the Ethernet Type number that indicates the ULP that this
frame should be sent to. This number is greater than 1500 (05DC hex).
Examples of EtherTypes are 0x0800 for the IP protocol and 0x6004 for
Dec LAT. A list of Ethernet types can be viewed at
www.standards.ieee.org/regauth/ethertype/type-pub.html.
Data
Contains ULP information.
Frame Check Sequence (FCS)
The FCS uses a 32-bit cyclic redundancy check (CRC) for error
detection.














Search WWH ::

Custom Search