Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Ethernet networks. Ethernet uses carrier-sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/
CD) as the access method.
CSMA/CD Media Access Method
CSMA/CD is the media access method on Ethernet networks. In this scheme, hosts listen to the
network for activity. If there is no network activity, hosts can transmit a frame onto the network,
while transmitting hosts listen to the network for any collisions with other transmitting nodes.
If no collision is detected, the host assumes that the frame transmitted successfully. If a collision
is detected, the node waits a random amount of time and listens for traffic on the segment. If
there is no traffic, it attempts to send the frame again. It attempts 16 times before sending an
error message to the upper-layer protocol (ULP).
You only use CSMA/CD in shared networks or hubs. If an Ethernet or FE interface is
configured for full-duplex operation, it does not use CSMA/CD. Because no collisions
are in full-duplex mode, CSMA/CD is not required.
NOTE
Ethernet Encoding
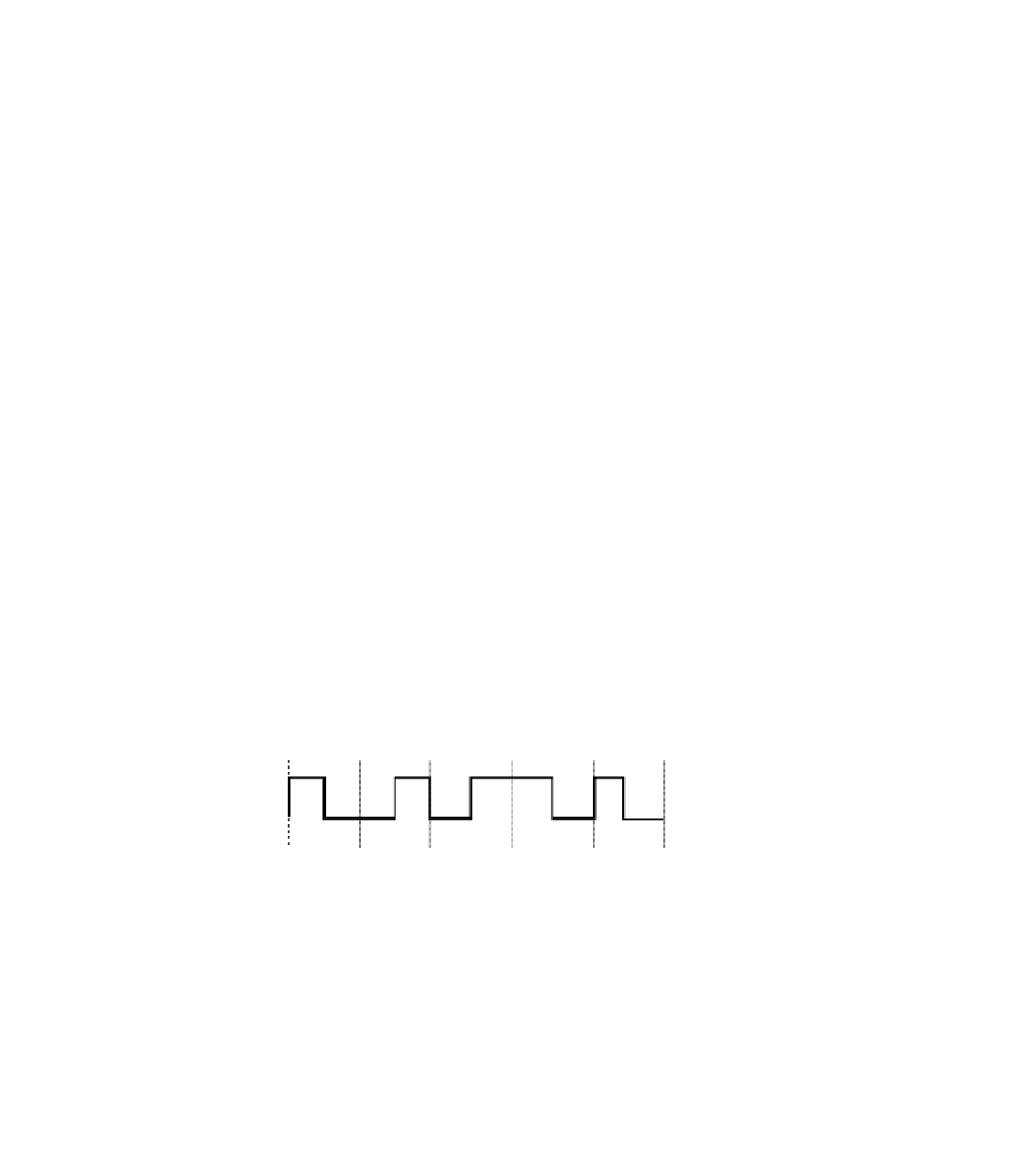
Manchester encoding was selected to code signals on the wire on Ethernet. In Manchester
encoding, a 0 is represented as a transition from high to low in the middle of the clocking time
interval. A 1 is represented as a transition from low to high in the middle of the time interval.
Figure 4-1 shows a sample of Manchester encoding.
Manchester encoding
Figure 4-1
0
1
1
0
0
Ethernet Frame Formats
After the Ethernet V2 standard was published, an effort went into producing an IEEE standard
for Ethernet. The IEEE 802 committee produced their 802.3 and 802.3 SNAP frame formats,
with the 802.2 Logical Link Control (LLC). Novell also produced a frame format for its net-
work operating system. These different groups produced different frame formats for the Ether-
net wire, but the signaling, encoding, and frame maximum and minimum sizes remain the same.














Search WWH ::

Custom Search