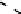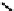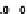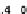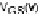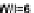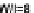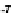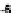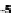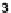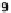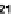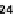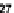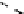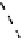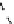Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
(a) Variation of
g
m
/I
D
for n-channel and
p-channel MOS transistor.
(b) Variation of
g
m
/I
D
with different as-
pect ratio.
Fig. 1.
Variation of
g
m
/I
D
Fig. 2.
Variation of
g
m
/I
D
with normalized current
amount of drain current flows, which implies small amount of power dissipation.
Therefore, by biasing the MOS transistor in the weak inversion region, it is
possible to obtain high gain with very small power dissipation.
2.1 Shortcoming of the Traditional Methodology
An important shortcoming of the traditional
g
m
/I
D
methodology is that it does
not explicitly considered the dependence of the Early voltage
V
A
on the operating
bias points (
V
DS
,V
GS
) of the transistor. The Early voltage is considered to
be constant depending upon the channel length. However, for nano-scale MOS
transistors, the Early voltage is found to be significantly dependent upon the
bias voltages. The intrinsic gain of a MOS transistor is dependent upon the
Early voltage, which in turn can be controlled by the operating bias points.