Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
Counter
scarp
Bulging
Foliation
dipping into
slope
Faults
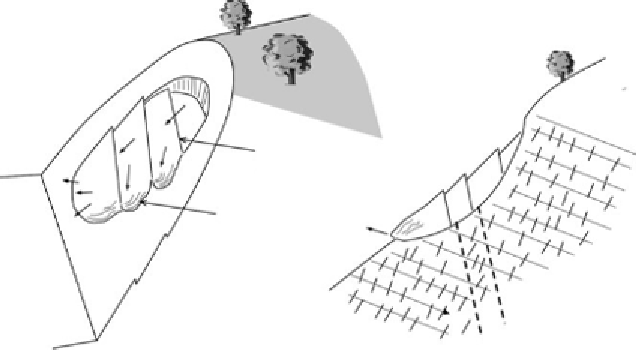
detailed face mapping by geologists, review of displacement data and
examination of the various stages of failure, a model was derived that
can be used to explain the nature of the failure, the vectors of
movement and the fact that it has not yet failed catastrophically but is
bulging at one section of the toe
(Figures 7.14
&
7.15)
. Key aspects of
the geology are frequent joints that are oriented roughly orthogonal to
the schistosity, three persistent faults cutting across the failure and
a)
c)
joint girdle
foliation
b)
rock
bridge
joint
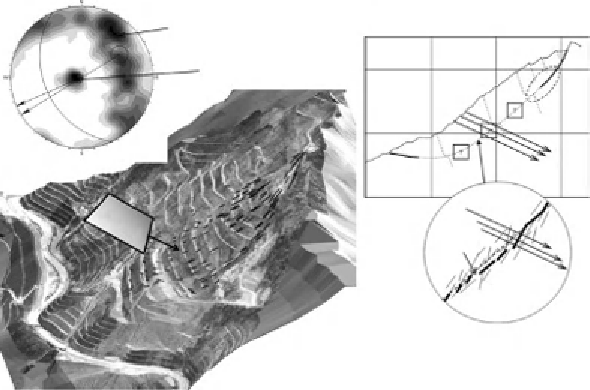
an orthophoto with an as-built CAD drawing (courtesy of Dr Andy Hansen). (b) Stereo plot with
concentration of poles near centre representing the foliation dipping back into the slope at about
14 degrees. Most joints form a girdle at about 90 degrees to the mean pole of the foliation. (c)
Explanation for main body of landslide
-
exploiting jointing and kicking out at the toe and upwards,
along foliation.