Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
14
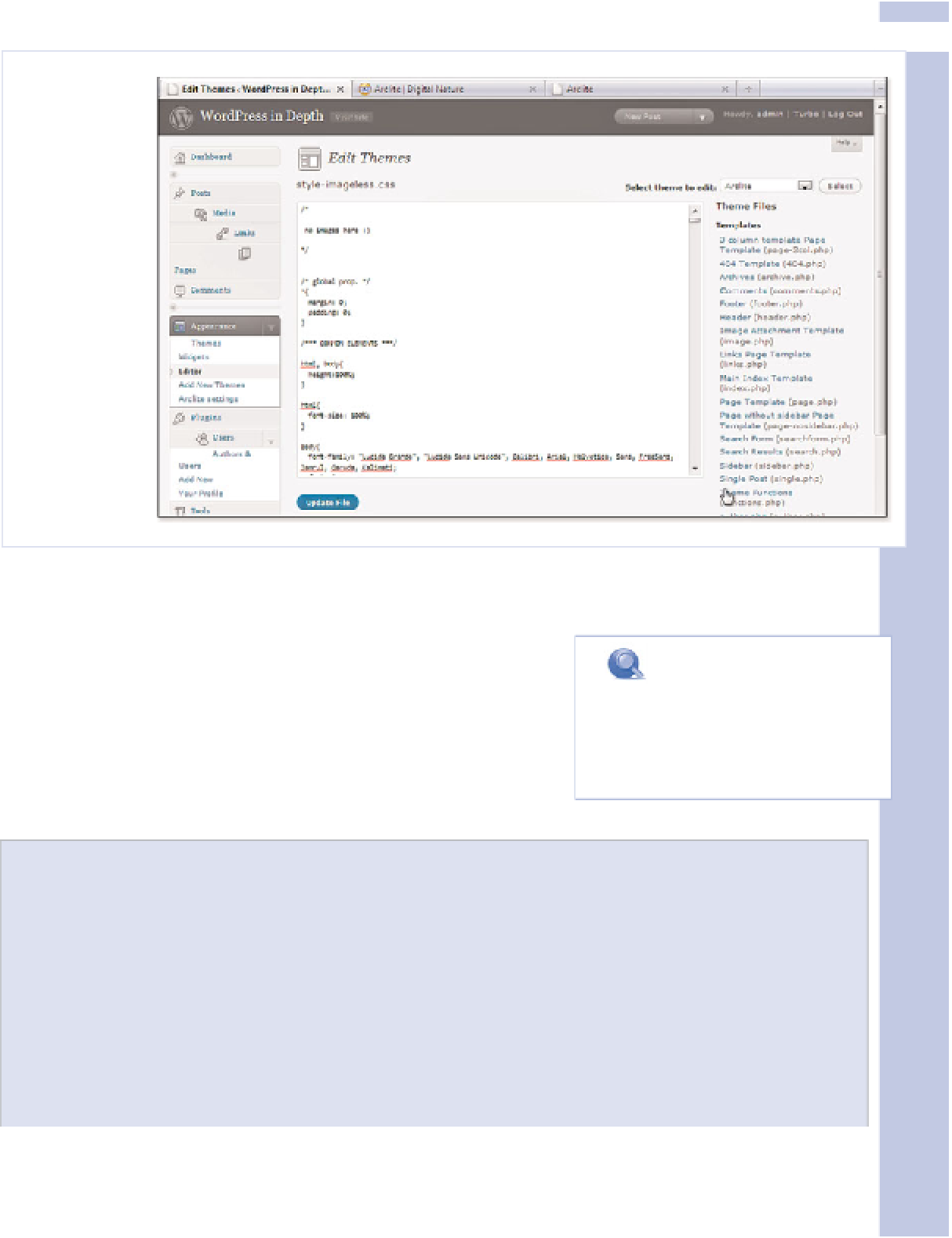
Figure 14.6
The Theme
editor lets
you play with
a theme's
CSS and PHP
files in the
familiar
WordPress
environment.
The Theme editor displays the files from your currently active theme by default. Use the Select
Theme to Edit box in the upper right of the Theme editor to edit a different theme.
There's no formatting toolbar in the Theme editor, as there's
nothing to format. There are no drop-down menus as in a set-
tings dialog box. You are expected to know what to do here.
As with the Post editor, when you make changes here, they
become part of your site the instant you click Update File. For
this and many other reasons, take care of your theme files.
note
Feel free to look at the PHP tem-
plates in the editor now. We look
more closely at the PHP side of
theming in Chapter 15.
Backing Up Themes to Preserve Your Choices
Preferences change. So do ideas of what looks good. For that matter, theme templates change too,
to plug security holes or offer more options. This is all to remind you to protect yourself and your
choices as you make changes to your theme.
The Theme editor does not allow you to save files with a different name. It only edits and updates
existing theme files. Before editing your theme templates and CSS, back up your default files. Use
your FTP program to place a copy on your own computer's hard drive. Rename any file on your
server you plan to edit (for example, call the original
style.css
file
theme-default.css
).
Continued…