Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
O
2
N
H
O
O
2
N
CO
2
CH
3
CO
2
CH
3
H
3
CO
2
C
H
3
CO
2
C
Hantzsc
h
CH
3
H
H
3
C
O
H
3
C
CH
3
O
NH
3
Nifedipine
O
2
N
CO
2
CH
3
O
2
N
H
O
2
N
O
CO
2
CH
3
H
2
N
H
3
CO
2
C
CH
3
H
3
CO
2
C
H
3
CO
2
C
H
3
C
H
CH
3
H
3
C
O
H
3
C
O
Nifedipine
Beta blockers represent another class of drugs used for hypertension.
They block beta-adrenergic receptors, preventing adrenaline (epinephrine)
from stimulating these receptors. In this manner, they slow the heart rate and
reduce the force with which the heart muscle contracts, thereby lowering
blood pressure. Examples include atenolol (Tenormin
®
, AstraZeneca),
carvedilol (Coreg
®
, Glaxo SmithKline), and metoprolol, sold as the tartrate
salt (Lopressor
®
, Novartis) or the succinate salt (Toprol
®
, AstraZeneca). For
each of these compounds, the carbon bearing the hydroxyl group is chiral
and they are all administered as racemic mixtures.
H
3
C
H
3
C
O
N
H
CH
3
O
H
CH
3
OH
OH
O
CH
3
Metopropol
CH
2
CONH
2
Atenolol
HO
OCH
3
O
O
HN
H
Carvedilol
Diuretics increase the rate of urine formation. One common class of
diuretics is the thiazide type represented by hydrochlorothiazide. The
thiazides affect the renal tubular mechanisms of electrolyte reabsorption
and therefore directly increase excretion of sodium and chloride ions.
Hypertension has been linked to high sodium ion content and diuretics are
used to combat hypertension by decreasing sodium levels. The thiazides





































































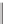

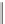











Search WWH ::

Custom Search