Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
article is formed by injection molding, upon cooling it shrinks and the dimen-
sions are slightly smaller than those of the mold. This is because the density
of a polymer increases as the temperature decreases. Shrinkage is greater in
crystalline polymers because with cooling as the crystallites form, the density
increases. Shrinkage can cause sink marks, voids, and residual stresses and
needs to be controlled. In extreme situations, the plastic part can warp or crack
due to the stresses. Some shrinkage can be controlled by injection molding
conditions and mold design. If the shrinkage is consistent, the size difference
can be compensated for by making the mold cavity appropriately larger when
the mold is first made. It is more of an issue when different formulations with
different amounts of shrinkage are processed in the same mold. For many
materials, there can be post-mold shrinkage as the article slowly anneals.
Impact modifiers are added to many formulations. As the name implies,
they impart toughness to the polymer article or film. Many of them are
butadiene copolymers that disperse in the polymer matrix. One type - the
so-called core shell modifiers - has a rubbery core surrounded by a harder
acrylate layer. They have been compared to an egg; soft on the inside and
hard on the outside. The outer shell also has some adhesion to the matrix
so that the modifier can be dispersed. Other impact modifiers include
methacrylate-butadiene-styrene copolymers or EPDM, ethylene-propylene-
diene monomer copolymers. Acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) and
ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) are also used.
Pigments are also common. Generally when a formulation is pigmented
it contains several pigments to give a color match. Carbon black is added to
make black formulations; white formulations are made with titanium dioxide.
For other colors, titanium dioxide is often added to provide a white base so
that minor differences in the yellowness of the polymer do not prevent a good
color match.
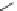
Some formulations contain nucleating agents to speed the crystallization of
the polymer. Agents such as sodium stearate or calcium stearate are used. One
type of nucleating agent is 1,3-O-2,4-bis(3,4-dimethylbenzylidene) sorbitol
[25] which provides good clarity for polypropylene.
OH
HO
O
HO
O
O
O
2
+
Ca
C
17
H
35
O
Na
C
17
H
35
O
OH
2
1,3-O-2,4-bis(3,4-dimethylbenzylidene) sorbitol
Sodium stearate
Calcium stearate
Plastic articles or films that come in contact with food might be formulated
with antimicrobial additives. Other applications that might use antimicrobial

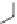












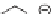

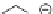






Search WWH ::

Custom Search